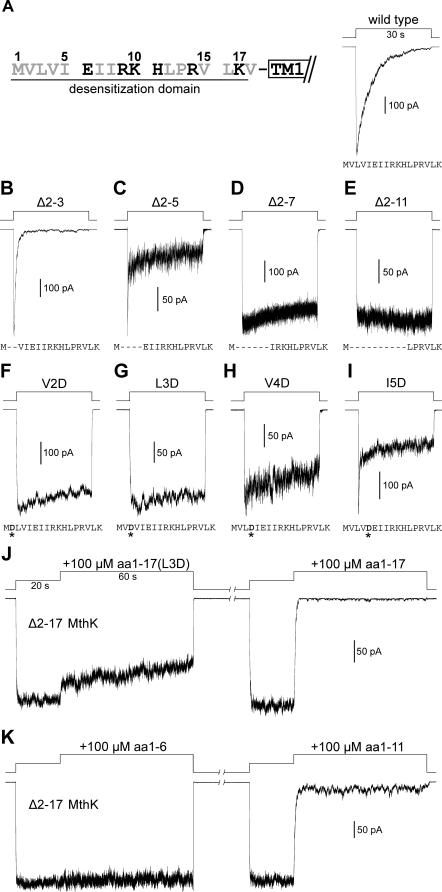
Figure 3. Mutational Analyses at the Cytoplasmic N-Terminus of MthK.
Activation was done by stepping the perfusate from EGTA to Ca20 solutions at pH 7.5. (A) Left, amino acid sequence of the N-terminal desensitization domain (DD) of MthK. Hydrophobic residues are shown in gray. Right, a typical macroscopic trace of wild-type MthK.
(B–E) Traces of sequential N-terminal deletion mutants show that truncations of DD result in significantly altered channel gating properties.
(F–I) Traces of single-point mutations (asterisks) at the initial hydrophobic residues of the DD show that introducing a charged aspartate residue to disrupt the initial hydrophobicity drastically alters the gating profile.
(J) Traces recorded from the same patch show the effects of 100 μM aa1–17(L3D) peptide (left trace) and aa1–17 peptide (right trace) on open Δ2–17 MthK channels.
(K) Traces from the same patch, containing Δ2–17 MthK channels, show the effects of the aa1–6 (left trace) and aa1–11 (right trace) peptides. Typical traces are shown, representing four to six independent patches for (B–K).