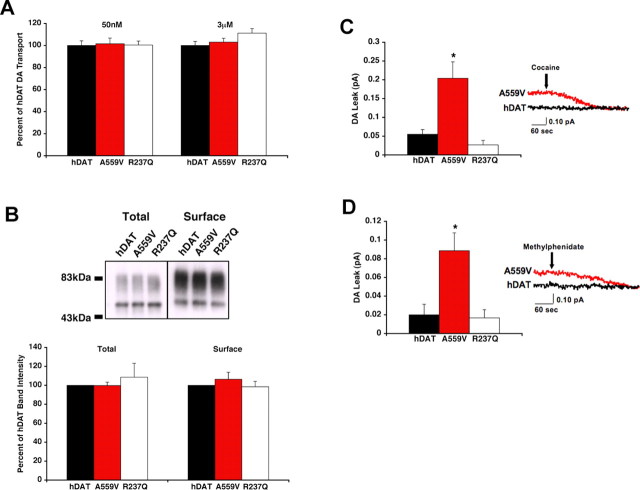
Figure 1.
hDAT A559V mutation produces cocaine- and MPH-sensitive DA efflux. A, Inward transport of 50 nm (n = 3) or 3 μm [3H]DA (n = 3) by hDAT or hDAT variants. DA transport activity is expressed as a percentage of that obtained with hDAT and reported as a mean ± SEM. Mean 50 nm DA hDAT transport activity was 8.89 × 10−18 ± 5.9 × 10−19 mol/cell/min and mean 3 μm DA hDAT transport activity was 2.85 × 10−16 ± 2.1 × 10−17 mol/cell/min. B, Top, Representative Western blot, using 40 μg of biotinylated protein or 4 μg of total cellular lysate. Bottom, Quantitation of total and surface hDAT protein expression (n = 3). C, hDAT A559V mediates enhanced outward DA leak. DA outward leak from hDAT (n = 4), hDAT A559V (n = 5), and hDAT R237Q (n = 3) cells is reported as mean amperometric current ± SEM. Cells were actively loaded with 1 μm DA, and DA leak was measured by amperometry as described in Materials and Methods; DAT specificity was defined by 10 μm cocaine. *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple-comparison test. D, DA outward leak from hDAT (n = 6), hDAT A559V (n = 7), and hDAT R237Q (n = 3) cells as defined by 10 μm MPH. *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple-comparison test. Traces provide examples of recordings under each condition.