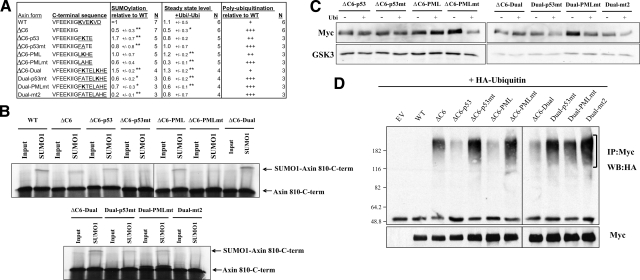
Figure 4.
The addition of exogenous SUMOylation sites restores the stability of Axin-ΔC6 and its resistance to ubiquitination. A) Sequences of the C-terminal regions of WT and mutant Axin. ΔC6-p53, ΔC6-PML, and ΔC6-Dual are constructs in which SUMOylation sites from p53 (FKTE including K386) PML (LKHE including K160), or both, were added to Axin-ΔC6; “mt” indicates site-directed mutants in which the lysine resides in the SUMOylation sites were replaced with alanine. SUMOylation motifs are underlined; lysine residues are shown in bold. Values are averages ± sd. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; t test: ΔC6 vs. WT, ΔC6-p53 or ΔC6-PML vs. ΔC6, ΔC6-p53mt vs. ΔC6-p53, ΔC6-PML-mt vs. ΔC6-PML, ΔC6-Dual vs. ΔC6, and D-p53mt, D-PMLmt and Dual-mt2 vs. Dual. Polyubiquitination levels are averages of three different experiments. B) In vitro SUMOylation assay with the indicated WT or mutant Axin fragments (amino acid 180 to the indicated C terminus). Average levels of SUMOylated Axin, normalized to wild-type Axin (set to 1), are indicated in A. Addition of one or both artificial SUMOylation sites to AxinΔC6 increased its ability to be SUMOylated, whereas mutation of the lysine residues reduced or eliminated this effect. C) Effects of ubiquitin on the stability of WT and mutant Axin. The indicated Myc-tagged Axin constructs (1 μg) were cotransfected with empty vector (–Ubi) or 1 μg of HA-ubiquitin vector (+Ubi), and the levels of Axin protein were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Myc. The protein level in the presence of ubiquitin was normalized to that without ubiquitin, for each construct. In comparison to AxinΔC6, which showed decreased stability with ubiquitin (Fig. 3C), the addition of the p53, PML, or both SUMOylation sites partially or completely restored its stability in the presence of ubiquitin. Replacement of the lysine residues within the SUMOylation sites with alanine reduced or abolished their effects on stability (with the exception of the lysine in the p53 site in construct ΔC6-p53mt, which showed highly variable results in different experiments). GSK3 was used as a loading control. D) Ubiquitination of AxinΔC6 variants, after cotransfection with HA-ubiquitin (as in Fig. 3D), was detected by Western blotting with anti-HA antibody. Polyubiquitinated forms of Axin are indicated by brackets. Average levels of polyubiquitinated Axin, from three experiments, are indicated in A. Addition of SUMOylation sequences from p53, PML, or both protected Axin-ΔC6 from excess ubiquitination, whereas mutation of the target lysine residues reduced or eliminated this protective effect, resulting in increased polyubiquitination.