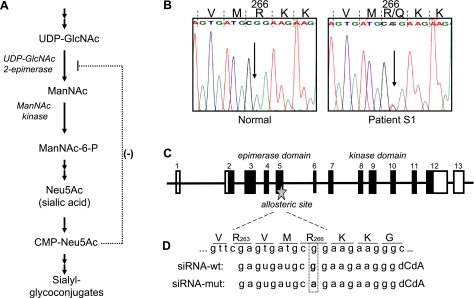
Figure 1.
Intracellular sialic acid synthesis, sialuria mutation, GNE gene structure, and design of allele-specific siRNA. A) The synthesis of sialic acid is initiated in the cytosol, where glucose undergoes several modifications to eventually become Neu5Ac (sialic acid). The reactions catalyzed by the UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase (GNE)/ManNAc kinase (MNK) bifunctional enzyme are the central and rate-limiting steps in this cytosolic process. GNE-epimerase activity is feedback inhibited by the downstream product CMP-Neu5Ac (CMP-sialic acid). CMP-sialic acid is utilized by the Golgi complex to produce sialyl glycoconjugates. B) The heterozygous GNE mutation, c.797G>A, in sialuria results in a R266Q missense amino acid change at the protein level. This mutation is located in the allosteric site of the GNE-epimerase enzymatic domain. C) Schematic of the GNE gene structure (not to scale). GNE consists of 13 exons, coding for the 722-aa protein GNE/MNK. The N-terminal part (exons 2–6) codes for the GNE-epimerase catalytic domain, including its allosteric site. The C-terminal part (exons 7–12) codes for the ManNAc-kinase catalytic domain. D) Schematic of the allosteric site of GNE/MNK, defined by amino acids R263 and R266, and design of the allele-specific siRNAs employed in this study.