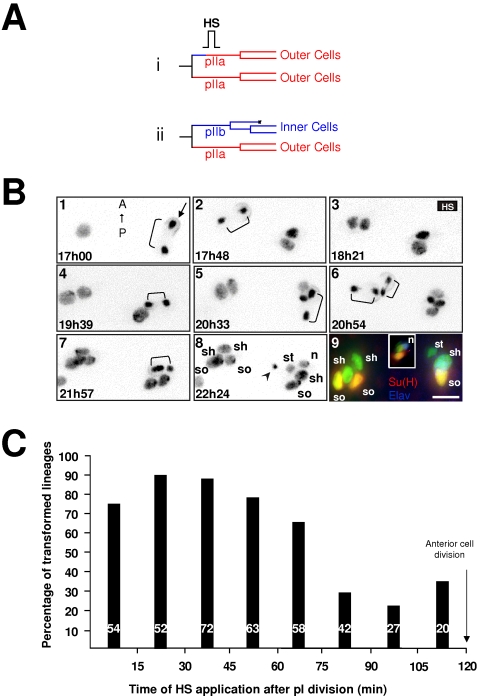
Figure 3. Cells are more receptive to ectopic N-pathway activation during their first hour of life.
A hs-Nintra pupae imaged in vivo was heat shocked (HS, 10 min at 37°C) at a given moment after pI division in order to ectopically activate the N-pathway in the anterior secondary precursor cell. (A) Lineages expected if the anterior secondary precursor cell responded or not to Notch activation (i and ii respectively). (B) Representative frames from an in vivo recording of two microchaete lineages of an hsNintra; neu>PON::GFP, H2B::YFP pupae in which a HS was applied between 18h16 to 18h26 APF. Anterior is on the top. Time APF is shown at the bottom left of each frame. The PON::GFP crescent was used to distinguish the polarity of each cell division (indicated only in frame 1, arrow). Brackets show cell divisions. The arrowhead in frame 8 indicates apoptosis of the glial cell. Each frame results from the merge of 7 horizontal optical sections. Frame 9 shows the final immunodetection. Su(H) in red, Elav in blue, sensory cells in green. The inset in frame 9 shows a lateral view of the right cluster highlighting the nucleus (n). Note that a normal sensory organ was generated when the HS was applied long after pI division (right cluster) whereas a sensory organ composed by outer cells exclusively is formed for earlier HS (left cluster). so, socket; sh, shaft; st: sheath, g: glial cell cells, n; neurone. Scale bar: 5 µm. (C) Percentage of sensory organs harboring two socket cells when the temperature shift was applied at different times after pI division (abscissa). Note that transformed sensory organs were observed when the HS was applied principally during the first hour of secondary precursor cells life.