Figure 6.
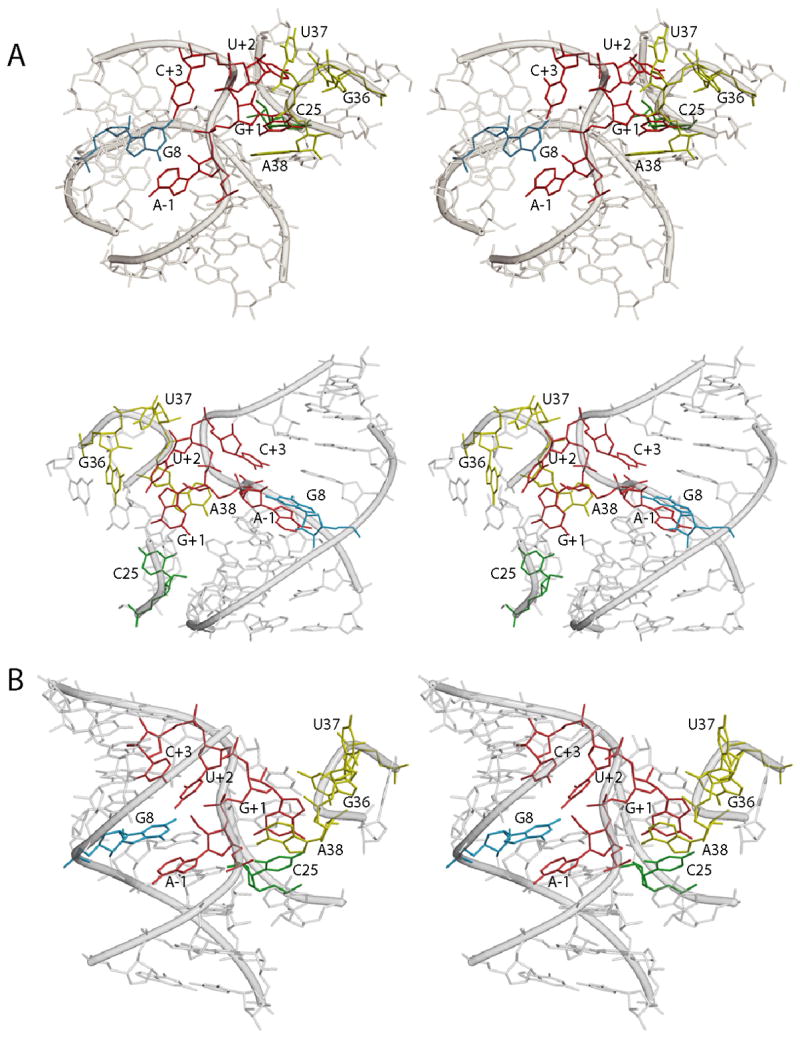
Models of the hairpin ribozyme active site. A) Two different stereo views of the MC-SYM-generated model based on biochemical and photochemical experiments. Residues A-1, G+1, U+2 and C+3 in the substrate strand are shown in red. G+1 which is stacking on A38 (yellow) and forming a Watson-Crick base pair with C25 (green) in the ribozyme 5′ strand. U+2 is bulged out of domain A and is in the vicinity of G36 and U37 (both in yellow) as suggested by crosslinking experiments. Residue C+3 forms a hydrogen bond with A7 and partially stack on G8 (blue). The latter nucleobase, in the substrate-binding strand, is stacked on A-1 and its Watson-Crick face is adjacent to the scissile bond. Remaining part of substrate and ribozyme strands are depicted in transparent gray. B) Stereo view of the crystal structure of the four-way junction hairpin ribozyme catalytic core.
