Abstract
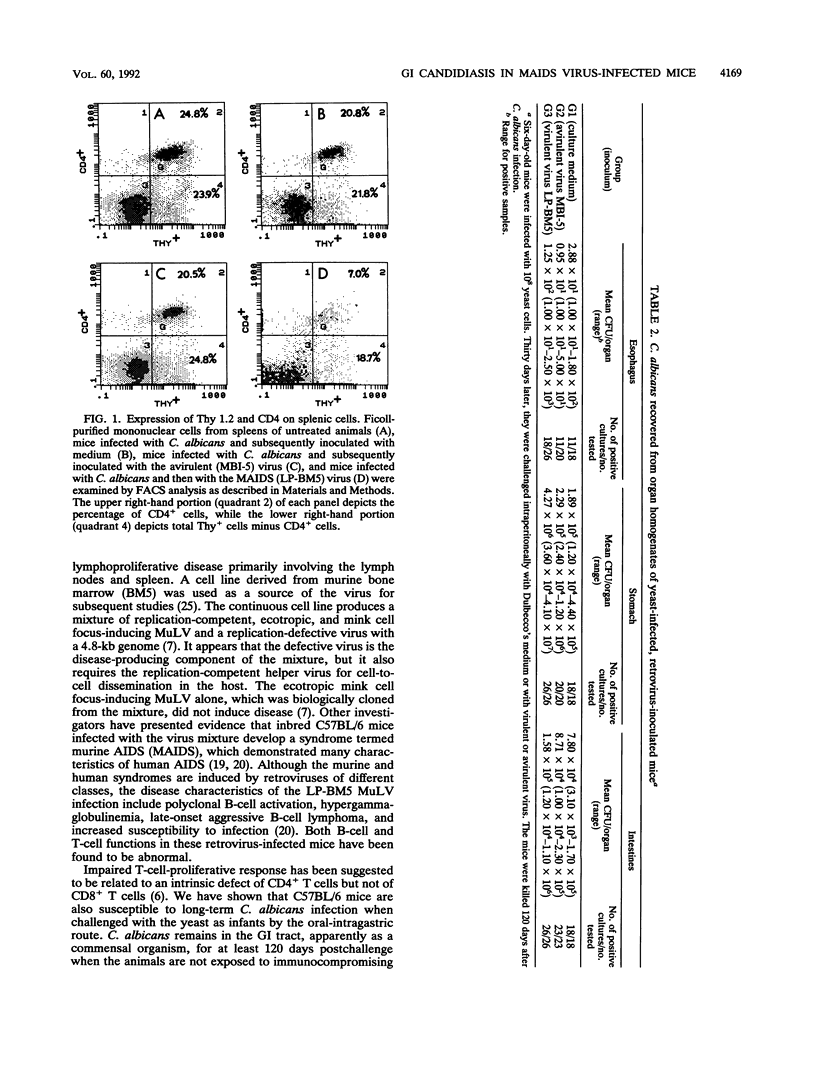
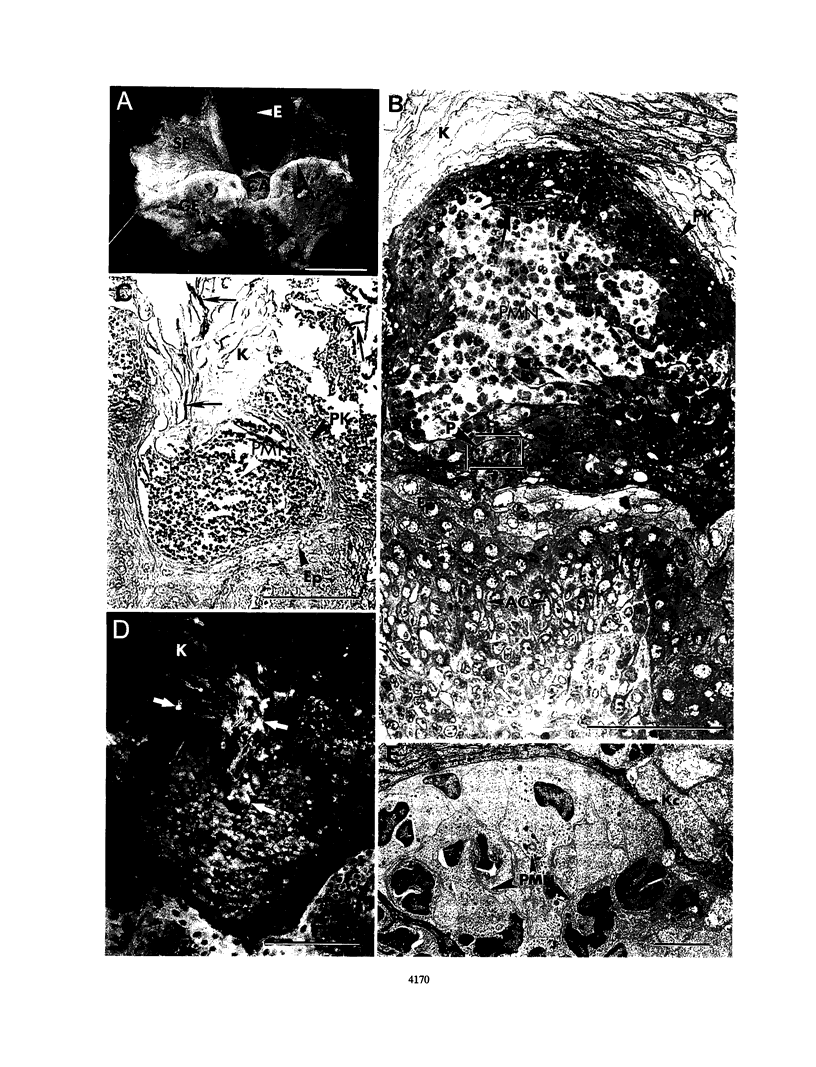
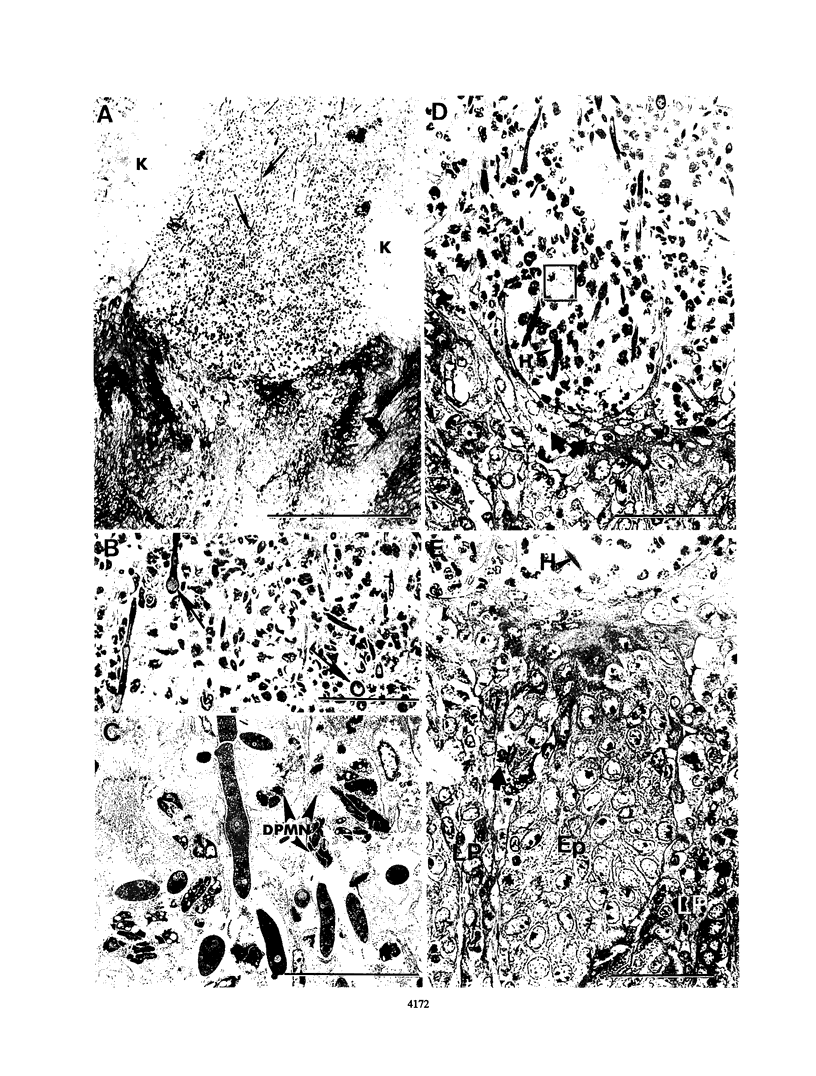
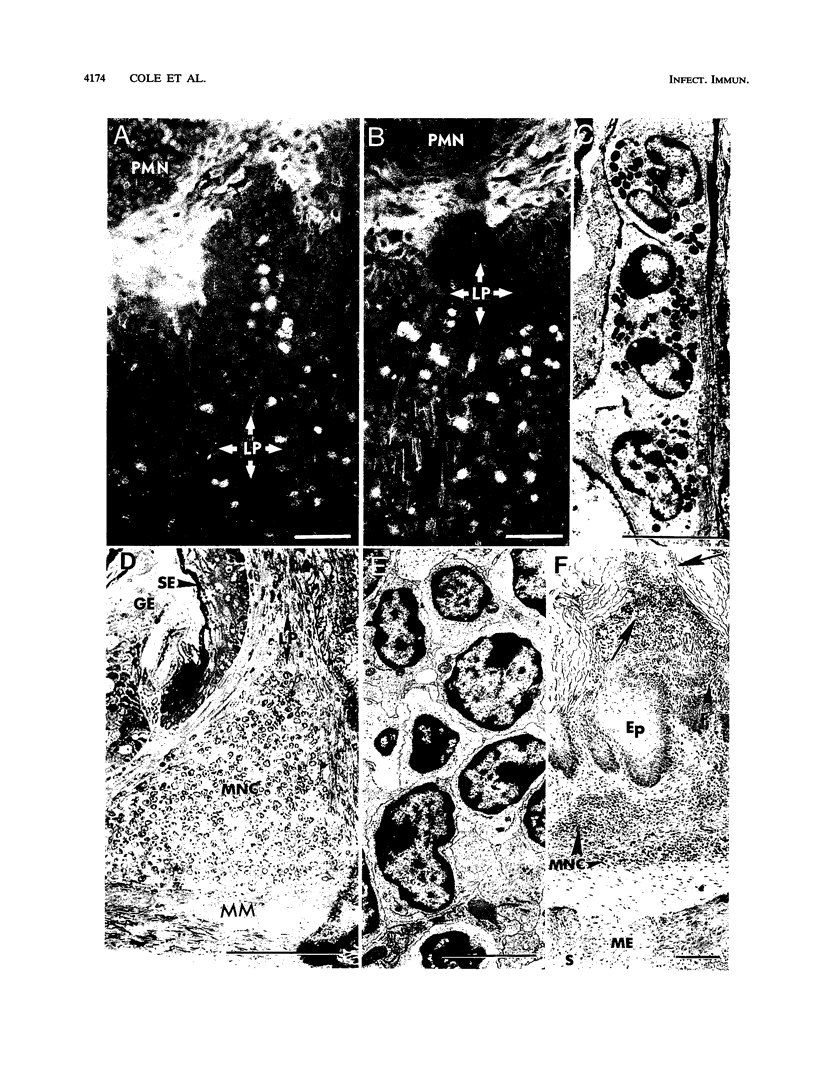
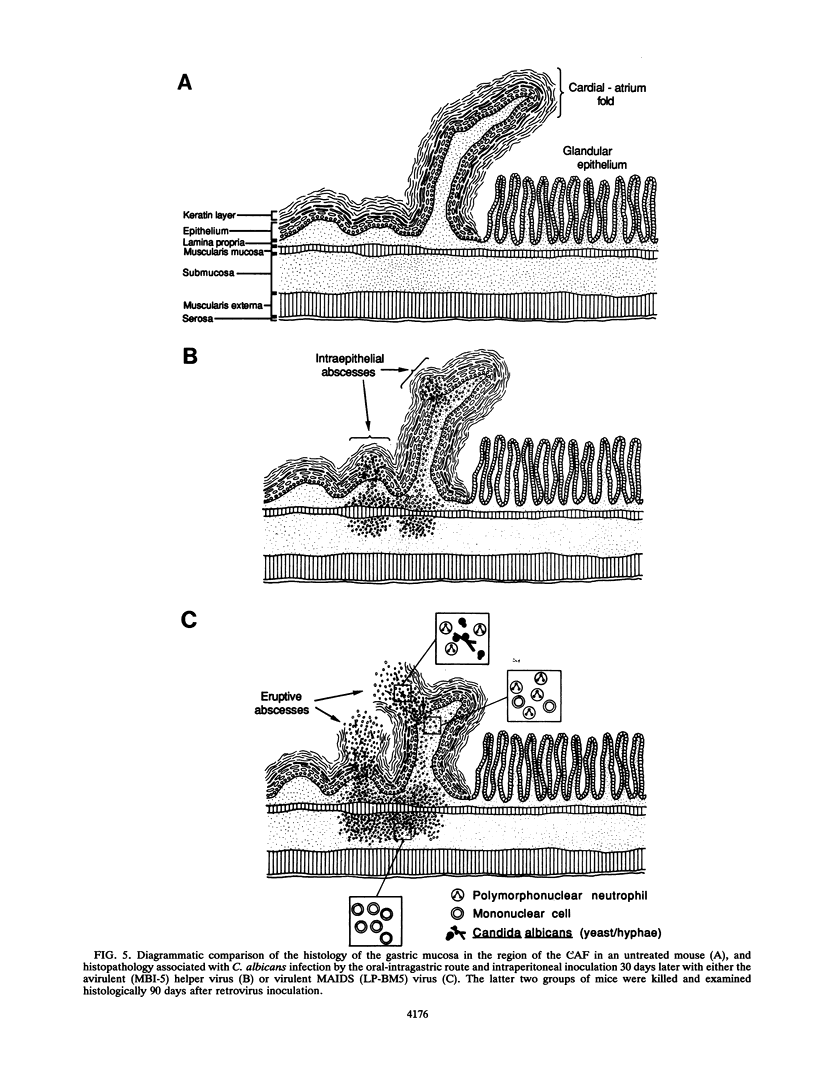
Dysfunction of neutrophils in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus is at least partly responsible for secondary microbial diseases in these individuals, including invasive gastrointestinal (GI) candidiasis. Immunoregulatory disturbances associated with the development of AIDS in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients exacerbates Candida albicans infection of the upper GI tract and frequently leads to oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis. In this article, we present the first report of a murine model of invasive GI candidiasis associated with an AIDS-related murine immunodeficiency syndrome that results from infection of C57BL/6 mice with a previously described retrovirus complex (LP-BM5). Mice of the inbred strain were infected with C. albicans by oral-intragastric inoculation as infants and with the retrovirus by the intraperitoneal route 30 days later. Control mice of the same strain were infected with C. albicans as above and subsequently infected with the avirulent, ecotropic helper virus (MBI-5). Animals were killed 90 days after retroviral challenge. Total and differential blood cell counts, CD4+ T-cell counts in the spleen, and the histopathology of the gastric mucosa of experimental and control animals were determined. The virulent LP-BM5-infected animals developed murine AIDS and showed eruptive and suppurative lesions, with associated C. albicans mainly in regions of the cardial-atrium fold of the stomach. Well-defined abscesses with entrapped C. albicans hyphae were observed in the region of the cardial-atrium fold of control mice. A significant increase in the number of C. albicans CFU in homogenized and plated segments of the GI tract was recognized in mice with murine AIDS versus the control animals. The murine model of GI candidiasis reported here permits examination of the nature of C. albicans interaction with the gastric mucosa both in the immunocompetent host under conditions in which the yeast exists predominantly as a commensal organism and in the immunosuppressed host during progressive stages of AIDS induced by a retroviral infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson J. S., Mills E. L. Depression of neutrophil function induced by viruses and its role in secondary microbial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):326–341. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz D. C., Hanna Z., Jolicoeur P. Severe immunodeficiency disease induced by a defective murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):505–508. doi: 10.1038/338505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Yetter R. A., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd Abrogation of resistance to severe mousepox in C57BL/6 mice infected with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):383–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.383-387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M. T., Balish E. Role of CD4+ lymphocytes in resistance to mucosal candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2447–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2447-2455.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Hügin A. W., Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ T cells in murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: evidence for an intrinsic defect in the proliferative response to soluble antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd, Makino M., Ruscetti S. K., Hartley J. W. Defective virus is associated with induction of murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. C., Chattopadhyay S. K., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd, Pitha P. M. Aberrant expression of cytokine genes in peritoneal macrophages from mice infected with LP-BM5 MuLV, a murine model of AIDS. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):121–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Lynn K. T., Seshan K. R. An animal model for oropharyngeal, esophageal and gastric candidosis. Mycoses. 1990 Jan;33(1):7–19. doi: 10.1111/myc.1990.33.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Lynn K. T., Seshan K. R. Evaluation of a murine model of hepatic candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1828–1841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1828-1841.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Lynn K. T., Seshan K. R., Pope L. M. Gastrointestinal and systemic candidosis in immunocompromised mice. J Med Vet Mycol. 1989;27(6):363–380. doi: 10.1080/02681218980000491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Phaneuf M., Lynn K. T. Chlamydospore-like cells of Candida albicans in the gastrointestinal tract of infected, immunocompromised mice. Can J Microbiol. 1991 Aug;37(8):637–646. doi: 10.1139/m91-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Pope L. M., Yancey R. J. Morphological aspects of gastrointestinal tract invasion by Candida albicans in the infant mouse. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988 Jun;26(3):173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E. Candida cell wall mannan: a polysaccharide with diverse immunologic properties. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(1):33–51. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. B., Kimura L. H., Menard T. W., Truelove E. L., Pearsall N. N. Effects of specific antibodies on the interaction between the fungus Candida albicans and human oral mucosa. Arch Oral Biol. 1982;27(6):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(82)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. SIV infected rhesus macaques: an AIDS model for immunoprevention and immunotherapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;251:279–293. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-2046-4_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Fredrickson T. N., Yetter R. A., Makino M., Morse H. C., 3rd Retrovirus-induced murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: natural history of infection and differing susceptibility of inbred mouse strains. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1223-1231.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P. Murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (MAIDS): an animal model to study the AIDS pathogenesis. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2398–2405. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATARJET R., DUPLAN J. F. Experiment and discussion on leukaemogenesis by cell-free extracts of radiation-induced leukaemia in mice. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1962 Aug;5:339–344. doi: 10.1080/09553006214550911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moors M. A., Jones S. M., Klyczek K. K., Rogers T. J., Buckley H. R., Blank K. J. Effect of Friend leukemia virus infection on susceptibility to Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1796–1801. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1796-1801.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. Animal models for retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease. Immunol Invest. 1986 May;15(3):233–261. doi: 10.3109/08820138609026687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Functional T lymphocytes are required for a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease (MAIDS). J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1737–1742. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Retroviral induction of acute lymphoproliferative disease and profound immunosuppression in adult C57BL/6 mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):766–784. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L. Gastrointestinal and disseminated candidiasis. An experimental model in the immunosuppressed rat. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981 Mar;105(3):138–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namikawa R., Kaneshima H., Lieberman M., Weissman I. L., McCune J. M. Infection of the SCID-hu mouse by HIV-1. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1684–1686. doi: 10.1126/science.3201256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Joyce W. A., Greenfield R. A. Gastrointestinal candidiasis in a murine model of severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2116–2119. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2116-2119.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nulsen M. F., Finlay-Jones J. J., McDonald P. J. T-lymphocyte involvement in abscess formation in nonimmune mice. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):633–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.633-636.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankhurst C., Peakman M. Reduced CD4 + T cells and severe oral candidiasis in absence of HIV infection. Lancet. 1989 Mar 25;1(8639):672–672. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M., Biegel D., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Abnormal regulation of IFN-alpha, -beta, and -gamma expression in MAIDS, a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3611–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha K., Wong P. K. ts1, a temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, can infect both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells but requires CD4+ T cells in order to cause paralysis and immunodeficiency. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2639–2646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2639-2646.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. E., Kasper D. L., Zaleznik D. F., Spriggs S., Onderdonk A. B., Finberg R. W. Cellular control of abscess formation: role of T cells in the regulation of abscesses formed in response to Bacteroides fragilis. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):341–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard C., Jolicoeur P. The effect of anti-neoplastic drugs on murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.1987646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanowitz H. B., Simon D., Wittner M. Medical management of AIDS patients. Gastrointestinal manifestations. Med Clin North Am. 1992 Jan;76(1):45–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Howard D. H., Ahmed R. Virus-induced immunosuppression: a murine model of susceptibility to opportunistic infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):232–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]