Figure 7. Concentration-dependent inhibition of acetaminophen glucuronidation by curcuminoid extract (A) and calphostin-C (B) in human liver microsomes and LS180 cells and of acetaminophen sulfation by curcuminoid extract (C) in human liver cytosol and LS180 cells.
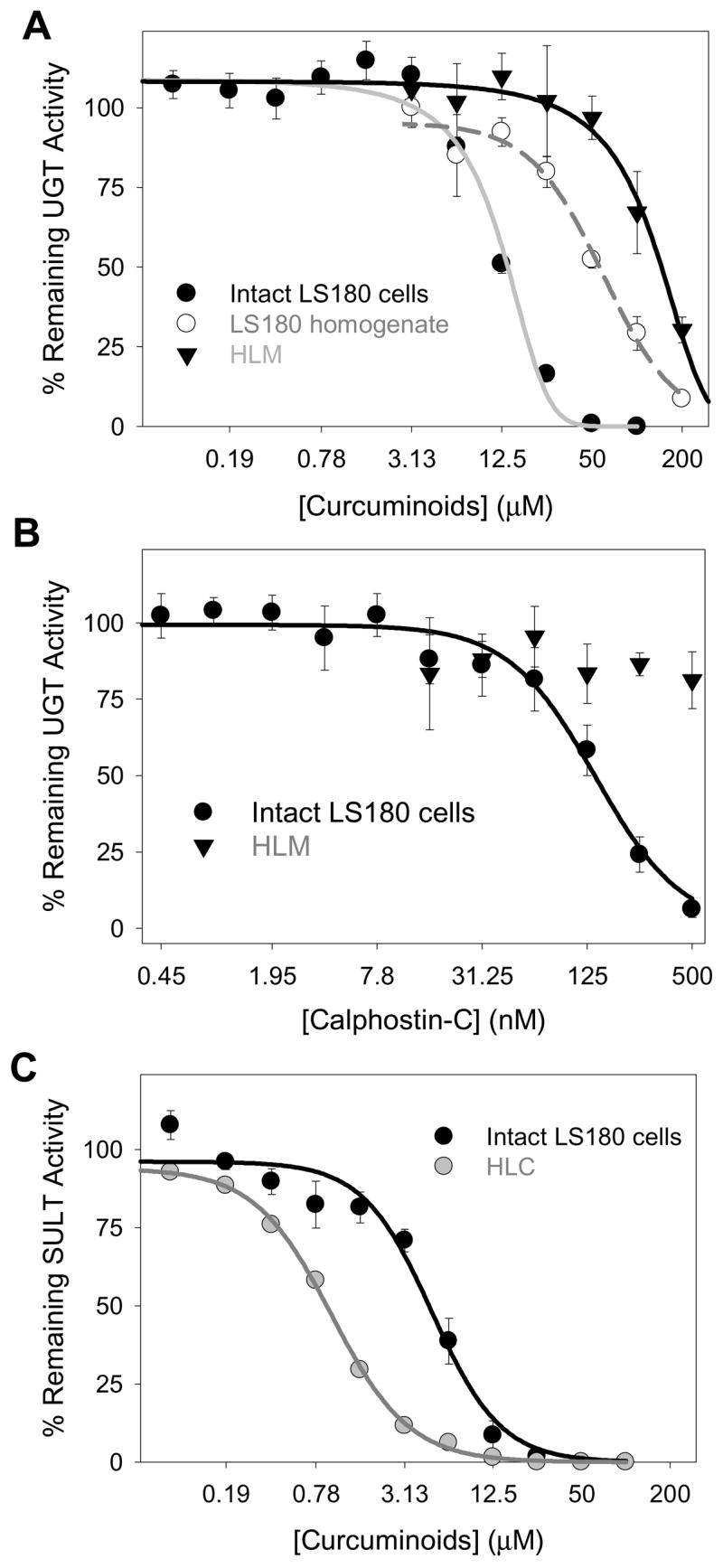
In panel A, inhibition of acetaminophen glucuronidation by curcuminoid extract was compared between intact LS180 cells, homogenates of (washed and untreated) LS180 cells, and human liver microsomes. In panel B, the effect of a selective PKC inhibitor, calphostin-C, on acetaminophen glucuronidation was evaluated using both intact LS180 cells and human liver microsomes. In panel C, inhibition of acetaminophen sulfation by curcuminoid extract was compared between intact LS180 cells and human liver cytosol. Methods section provides detailed assay information. Data points correspond to the mean ± standard error of at least three determinations. LS180 experiments were repeated on three different days.
