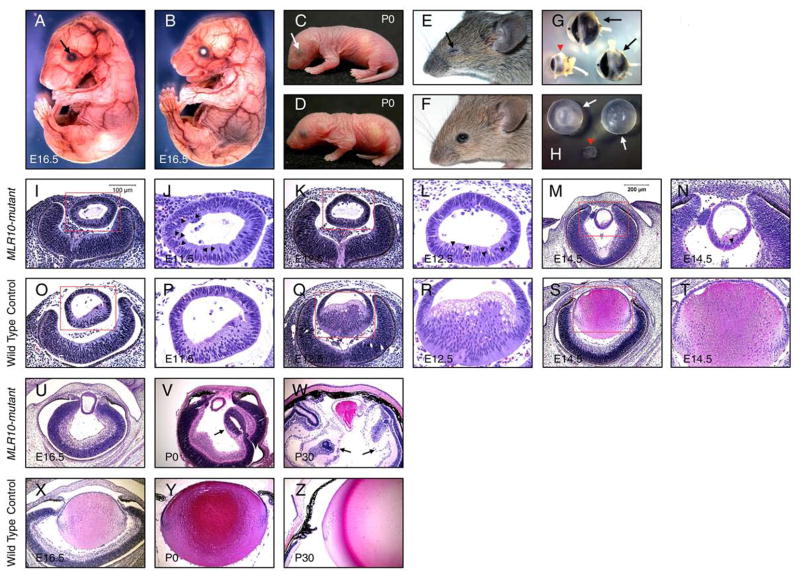
Figure 2.
Defective lens fiber elongation in MLR10-mutant (MLR10/Fgfr1flox/flox Fgfr2flox/flox Fgfr3 −/−) mice. A–F: MLR10-mutant mice (A, C, E) were compared with control mice (B, D, F) at E16.5 (A, B), P0 (C, D) and P30 (E, F). Triple Fgfr-deficient mice were characterized by severe microphthalmia (arrows A, C, E); G: Eyes of MLR10-mutant (arrowhead, G) were placed together with control eyes (arrows, G). The anterior chamber (*) is absent in the mutant eye; H: Lenses from MLR10-mutant mice (arrowhead, H) were much smaller than control lenses (arrows, H); I-Z: Histological analysis of MLR10-mutant (I–N, U–W) and control (O–T, X–Z) eyes. Developmental stages studied include E11.5 (I, J, O, P), E12.5 (K, L, Q, R), E14.5 (M, N, S, T) E16.5 (U, X), P0 (V, Y) and P30 (W, Z). The boxed regions in I, O, K, Q, M, S are shown at higher magnification in J, P, L, R, N, T respectively and pyknotic nuclei are indicated by arrowheads (J, L, N). Arrows in V and W indicate abnormal folds of neural retina in the mutant eyes.