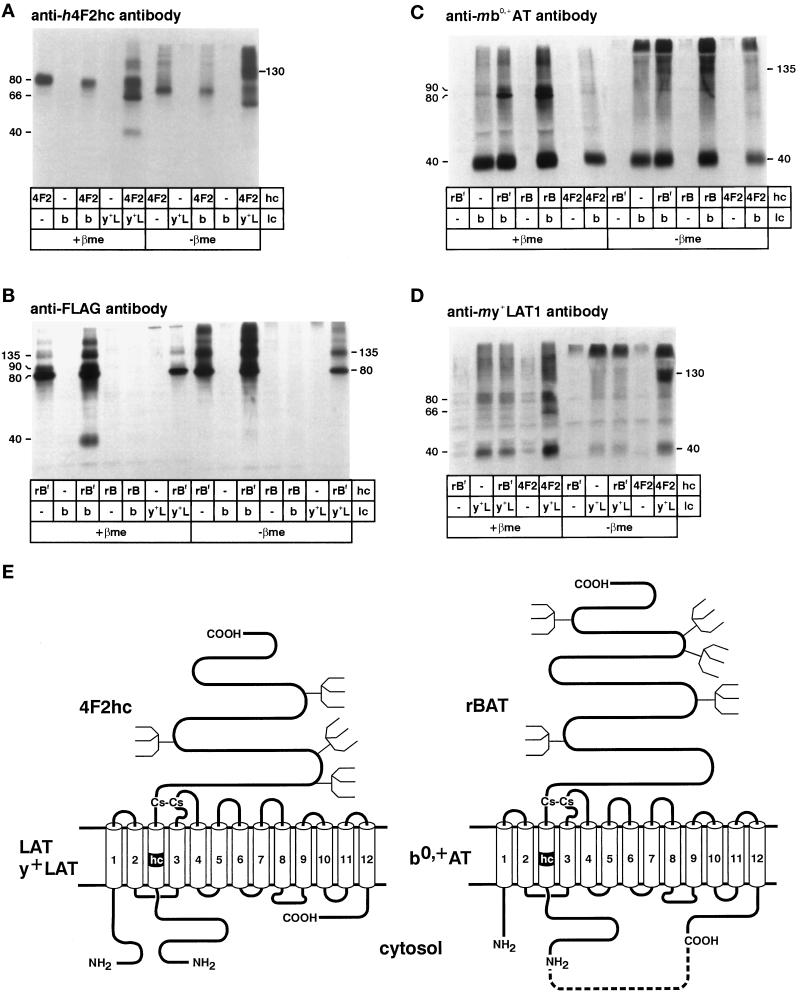
Figure 2.
Selective coimmunoprecipitation of mb0,+AT with hrBAT (or hrBATFLAG) and of my+LAT1 with h4F2hc. Oocytes were injected with cRNA for a heavy chain (hc) (rBf = hrBATFLAG; rB = hrBAT; 4F2 = h4F2hc) and/or a light chain (lc) (b = mb0,+AT; y+L = my+LAT1) as indicated. (A) From oocytes expressing h4F2hc alone, anti-h4F2hc antibody precipitated a protein migrating as two bands of ∼66 and ∼80 kDa that correspond to the core- and terminally glycosylated forms of h4F2hc. As expected, coexpressed my+LAT1 was coprecipitated with h4F2hc and migrated as an additional band of ∼40 kDa when the sample was treated with the reducing agent β-mercaptoethanol (β-me) and as a heterodimeric complex of ∼130 kDa in its absence. In contrast, there was no coprecipitation of mb0,+AT with h4F2hc. (B) Anti-FLAG antibody precipitated a protein migrating as two bands of ∼80 and ∼90 kDa that presumably represent the core-glycosylated and the terminally glycosylated forms of hrBATFLAG. When the oocytes coexpressed mb0,+AT with hrBATFLAG, an additional band of ∼40 kDa was coprecipitated. In nondenaturing conditions, the proteins remained assembled mainly as heterodimers and migrated at a level of ∼135 kDa. my+LAT1 was not coprecipitated with rBATFLAG. (C) mb0,+AT was immunoprecipitated by anti-mb0,+AT antibody (∼40 kDa), and hrBAT and hrBATFLAG were coprecipitated and appear as additional bands of ∼80 and ∼90 kDa (compare with B). h4F2hc was not coprecipitated with mb0,+AT. (D) my+LAT1 was immunoprecipitated by anti-my+LAT1 antibody (∼40 kDa), and additional bands of ∼80 and ∼90 kDa corresponding to coprecipitated h4F2hc appeared when h4F2hc was coexpressed (compare with A). hrBAT was not coprecipitated with my+LAT1. (E) Scheme of the heterodimers formed by the heavy chain 4F2hc with LAT or y+LAT light chains and of the heterodimers formed by rBAT with b0,+AT. The single evident transmembrane domain of the heavy chains is labeled hc, and the 12 putative transmembrane domains of the lipophilic light chain are numbered 1–12. The dotted line between the COOH terminus of b0,+AT and the NH2 terminus of rBAT represents the linker sequence introduced to form a functional fusion protein. The localization of the conserved cysteine residues forming the intermolecular disulfide bond has been demonstrated for the heavy chain 4F2hc and the light chains Xenopus LAT1 (ASUR4) and Schistosoma mansoni SPRM1 (Pfeiffer et al., 1998). Potential N-glycosylation sites are indicated by forks.