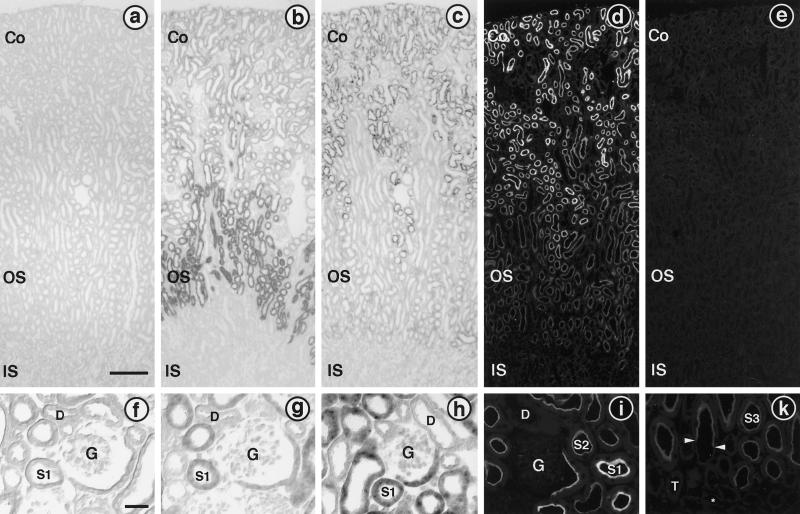
Figure 7.
Distribution of rBAT and b0,+AT in mouse kidney. Panels a–e show overviews of the cryosections (bar in a, 200 μm), and panels f–k show higher magnifications (bar in f, 50 μm). (a–c and f–h) In situ hybridizations. (b) Hybridization with a digoxigenin-labeled rBAT antisense riboprobe shows a strong signal in the outer stripe (OS) of the outer medulla, consistent with the previously reported preferential localization of rBAT mRNA in the S3 segments of proximal tubules. Weaker staining is also visible in proximal tubule profiles located in the renal cortex (Co), representing S1 and S2 segments. No staining is seen in the inner stripe (IS) of the outer medulla. (c) An inverse staining pattern is found in kidney sections hybridized with a b0,+AT antisense riboprobe. Proximal tubules in the renal cortex are heavily stained, whereas only very weak staining is detectable in the medullary rays and in the outer stripe. However, the hybridization signal at these locations is higher than in the adjacent inner stripe and is clearly above the level obtained from sections hybridized with a digoxigenin-labeled b0,+AT sense riboprobe (a). Higher magnifications of the renal cortex confirm the presence of rBAT mRNA (g) and b0,+AT mRNA (h) in the S1 segments of proximal tubules, starting from the first S1 cells at the urinary pole of the glomerulus (G), whereas other cell types within the glomerulus and distal tubules (D) are unstained. No signal is detected in the corresponding control section hybridized with a rBAT sense riboprobe (f). (d, e, i, and k) Immunofluorescence. (d) Immunohistochemical detection of b0,+AT at low magnification shows a bright immunofluorescent signal in proximal tubules within the renal cortex. Immunostaining, although at a lower intensity, is also visible in proximal tubules in the outer stripe. Preincubation of the antiserum with the antigenic peptide abolished the immunostaining completely (e). Higher magnifications of the cortex (i) and the outer medulla (k) show that b0,+AT is exclusively present in the brush border at the luminal pole of proximal tubular cell from S1 (i) to S3 (k). Arrows in panel k point to the abrupt transition from an S3 segment (with the stained brush border) to a thin descending limb (unstained). Note the decreasing staining intensities from S1 to S2 to S3. The immunofluorescent staining of the brush border of the proximal tubule at the urinary pole of the glomerulus (G) is slightly weaker than farther downstream in S1. Cells within the glomerulus, cortical distal tubules (D) (i), medullary thick ascending limbs (T) (k), and thin descending limbs (asterisk) (k) are not labeled with the antiserum.