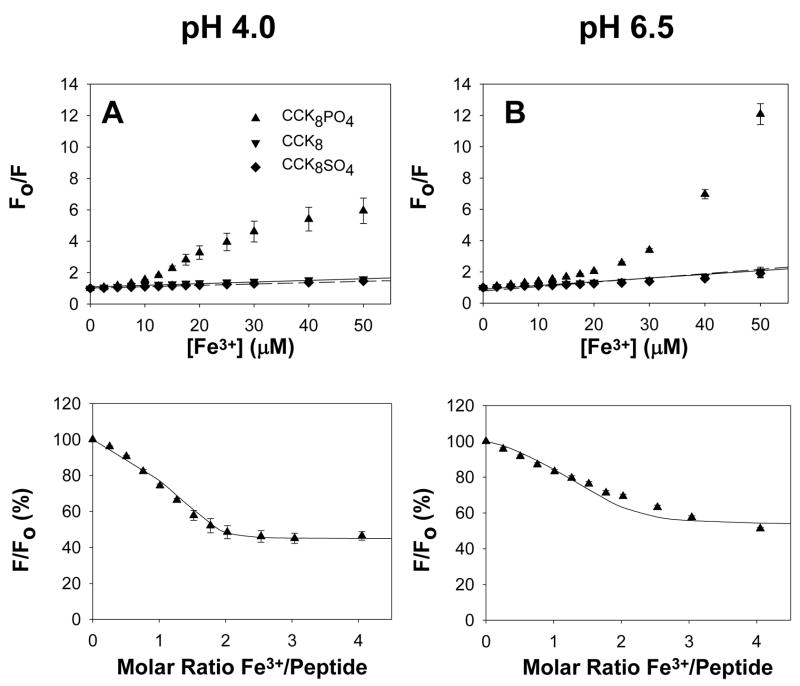
Figure 2. Ferric ions reduce CCK8PO4 fluorescence.
At pH 4.0 (A) or pH 6.5 (B) addition of aliquots of ferric chloride to 10 μM CCK8 (▼, solid line), or CCK8SO4 (◆, dashed line) in the buffers described in the Figure 1 legend resulted in a decrease in fluorescence that was well fitted by the Stern-Volmer equation. In contrast on addition of aliquots of FeCl3 to 10 μM CCK8PO4 (▲) the decrease in fluorescence was greater than predicted by the Stern-Volmer equation. The points in (C) and (D) were obtained by correction of the experimental data from (A) and (B), respectively, for the collisional component of quenching by subtraction. The lines were constructed by fitting the values for the reduction in fluorescence on occupation of the first (pH 4.0, 0.773; pH 6.5, 0.949) and second (pH 4.0, 0.448; pH 6.5, 0.528) sites with the program BioEqs, using the dissociation constants presented in Table 1 which had been obtained from fitting the absorbance data at the appropriate pH. Data are expressed as a percentage of the absorbance of that peptide without ferric ions. Points are means of at least three separate experiments; bars represent the SEM.