Figure 2.
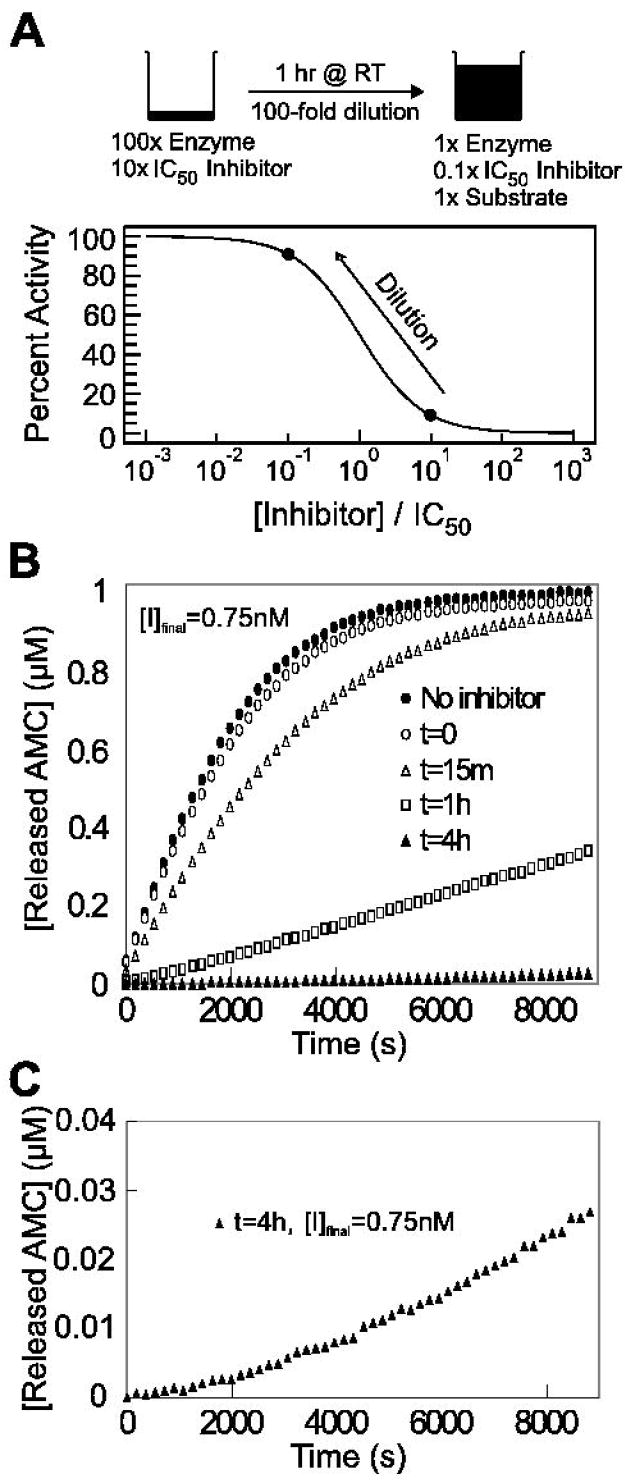
A. Dilution protocol for determination of reversibility. Cathepsin L at 100-fold its final assay concentration (870 ng/mL) and inhibitor at 10-fold its IC50 after 1 hr preincubation (75 nM) were combined and incubated for 1 hr at room temperature at 2 μL. This mixture was then diluted 100-fold with assay buffer containing 1 μM Z-Phe-Arg-AMC. A rapidly reversible inhibitor should dissociate from the enzyme to restore greater than approximately 90% of enzymatic activity. B. Reversibility data for SID 26681509 after 0 min (○), 15 min (Δ), 1 hr (□), and 4 hr (▲) preincubation with cathepsin L and upon 100-fold dilution into assay buffer containing Z-Phe-Arg-AMC. A full enzyme-substrate reaction without inhibitor (●) served as a positive control. By comparing initial substrate conversion rates of the control and 1 hr preincubation study, it can be seen that only 11% enzymatic activity is restored after 6000 s, making SID 26681509 a slowly reversible inhibitor of human cathepsin L. C. Reaction progress curve with 4 hr preincubation of cathepsin L and SID 26681509. This upward curvature demonstrates that the enzyme is recovering and the reaction is reversible. The rate of AMC release after 8820 s was 4.7 times greater than the initial release rate.
