Figure 6.
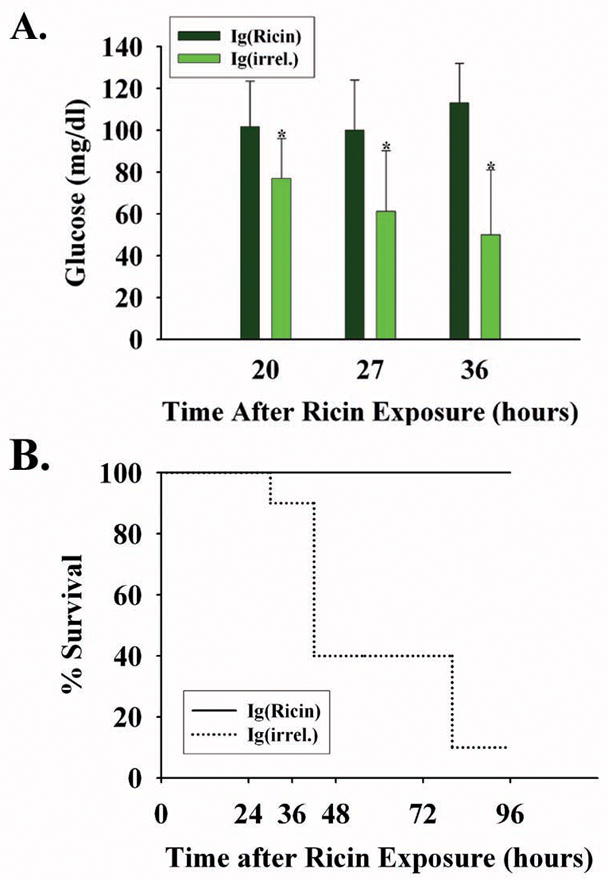
Blood glucose and lethality after pre-treatment with monoclonal immunoglobulin to ricin A chain. Mice were injected intravenously with monoclonal immunoglobulin to ricin A chain (RAC 17, 18 and 23; 20 μg/mouse each; N=10) or with irrelevant immunoglobulin matched for isotype and quantity (N=10) one hour prior to challenge with the ricin holotoxin (40μg/kg). A. Blood glucose levels (mean +/− 1 SD) at three intervals after ricin injection. *, p < 0.02, comparing RAC- versus irrelevant antibody-injected mice at 20, 27 and 36 hours following ricin challenge. B. Percentage of mice pre-treated with immunoglobulin which survived lethal ricin exposure. Ig(ricin) mice received 20 μg each of RAC 17, 18, and 23; Ig(irrel) mice were administered monoclonal IgG1 and IgG2A in the same quantity and in the same proportion as was received by the experimental group.
