Figure 8.
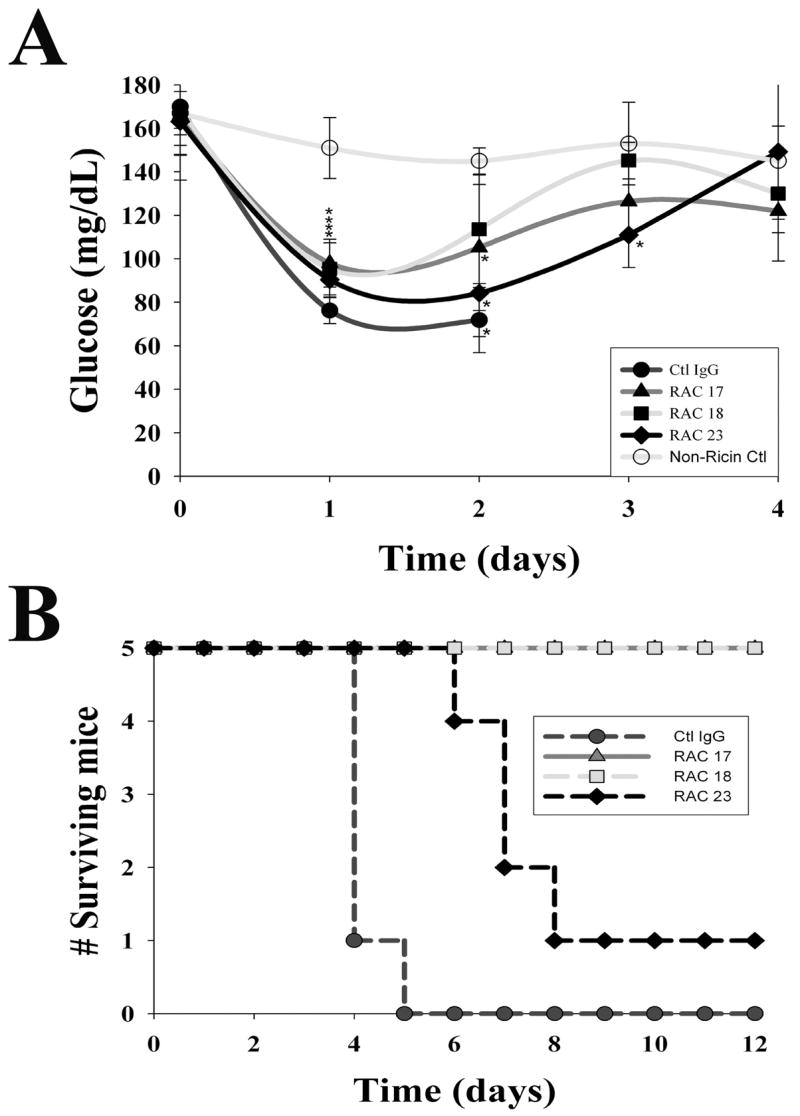
Maintenance of glucose homeostasis and host survival after administration of individual monoclonal antibodies to ricin A chain. Six hours following ricin challenge (40 μg/kg), mice were intravenously given 20 μg of a single immunoglobulin (RAC 17, 18, 23, or irrelevant IgG), then monitored for blood glucose every 24 hours and followed for survival. The data are representative of two independent studies. A. Blood glucose by treatment group (N=5/group) and shown as the mean +/− 1 SD. Glucose values in all groups of ricin-challenged mice diminished on day 1 before normalizing by day 3–4. * indicates p < 0.05, comparing ricin and antibody treated mice with non-ricin controls. Mortality in the irrelevant IgG group after day 2 was large, and the group mean blood glucose was not calculated. B. Survival among mice administered a single monoclonal immunoglobulin. Groups of mice were followed, with early deaths occurring among mice receiving control IgG, and a later loss of mice in those administered RAC 23. Mice not challenged with ricin are shown as ‘non-ricin controls.’
