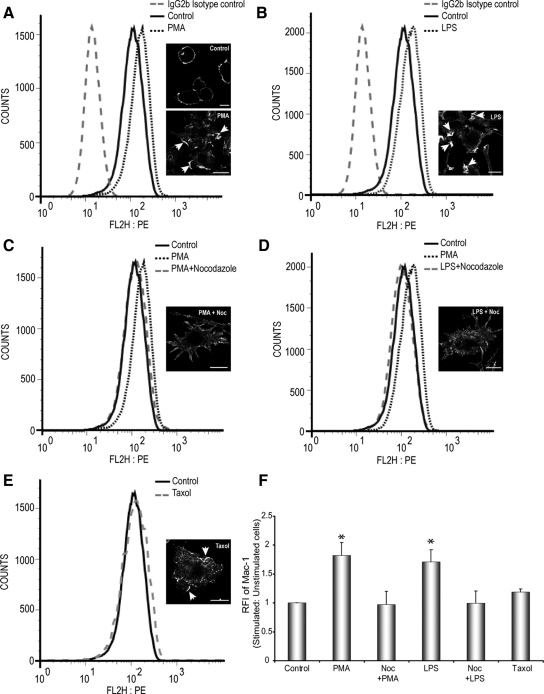
Figure 4.
PMA and LPS increase surface Mac-1 expression in a MT-dependent manner. Cell surface expression of Mac-1 in stimulated and unstimulated RAW264.7 macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry using a mAb against Mac-1. (A and B) Stimulation of RAW264.7 macrophages with 150 nM PMA or 10 μg/ml LPS, respectively, caused an up-regulation of cell surface Mac-1 expression compared with unstimulated cells and cells stained for isotype control. Insets, Mac-1 immunostaining for all conditions; arrows indicate ruffles. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C and D). Pretreatment of Noc in the presence of PMA or LPS inhibits the up-regulation Mac-1 expression on the surface of RAW264.7 cells. (E) Treatment of cells with taxol alone only induces a slight increase in the levels of Mac-1 expression, compared with untreated control cells. (F) Quantitative evaluation of the relative fluorescent intensities (RFI) of stimulated versus unstimulated (control) RAW264.7 macrophages. Data represents mean and SEM from three separate experiments. * p < 0.05 compared with control, untreated cells.