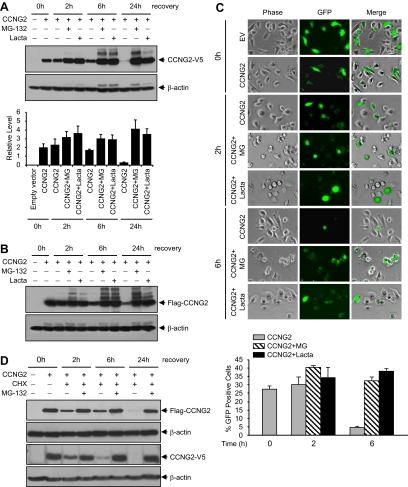
Figure 2.
Proteasome inhibitors increase cyclin G2 levels. (A) Expression of CCNG2-V5 in the absence or presence of proteasome inhibitors. OV2008 cells were transiently transfected with 3 μg/ml/well of CCNG2-V5 plasmid in six-well plate for 16 h and recovered in the presence or absence of 50 μM MG-132 or lactacystin for 0–24 h. Cyclin G2 was detected using an antibody against V5. A representative Western blot and a graph with normalized densitometry data (mean±SEM of three experiments) are shown. (B) Expression of Flag-CCNG2 at the same conditions as in A. Cyclin G2 was detected using an antibody against Flag. (C) OV2008 cells were transiently transfected with pCCNG2-GFP or empty vector (EV) for 16 h. GFP-positive cells were determined by fluorescence microscopy at 0, 2, or 6 h after transfection in the presence or absence of MG-132 or lactacystin. A histogram represents the percentage of CCNG2-GFP–positive cells in total cells. At least 800 cells were counted from each individual experiment, and data represent mean±SEM of three experiments. (D) OV2008 cells were transfected with either the Flag-CCNG2 pr CCNG2-V5 plasmid for 16 h and then treated with cycloheximide (CHX, 5 μg/ml) alone or together with MG-132 (10 μM) for 2–24 h. MG-132 prevented the degradation of cyclin G2.