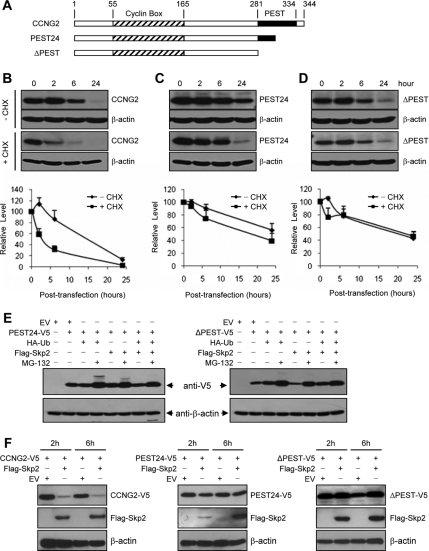
Figure 4.
PEST motif is involved in cyclin G2 stability. (A) Schematic presentation of cyclin G2 structure. Full-length cyclin G2 contains 344 amino acids. PEST24 is a half-PEST mutant which contains the first 24 amino acids of PEST. Mutant ΔPEST contains no PEST. (B–D) Stability of cyclin G2 and its PEST deletion mutants. OV2008 cells were transiently transfected with the full-length, partial or full PEST deletion of CCNG2 plasmids and recovered for 2–24 h in the presence or absence of cycloheximide (CHX). Representative blots are shown. Graphs represent densitometry data of four experiments. The expression of cyclin G2 peaked at 2 h and declined thereafter. Compared with the full-length cyclin G2, the PEST deletion mutants were relatively more stable. (E) MG-132 increased the levels of PEST deletion mutants. Cells were transfected with PEST24 (left panels) or ΔPEST (right panels), ubiquitin, and Skp2 for 16 h and then incubated with or without MG-132 for 6 h. (F) Effect of Skp2 on cyclin G2 and its PEST deletion mutants. Cells were cotransfected with Skp2 and cyclin G2 or its PEST mutants for 16 h and recovered for 2 or 6 h. Expression levels of cyclin G2 or its mutants were assessed by Western blotting probed with an anti-V5 antibody. Expression of Skp2 was detected using an anti-Flag antibody.