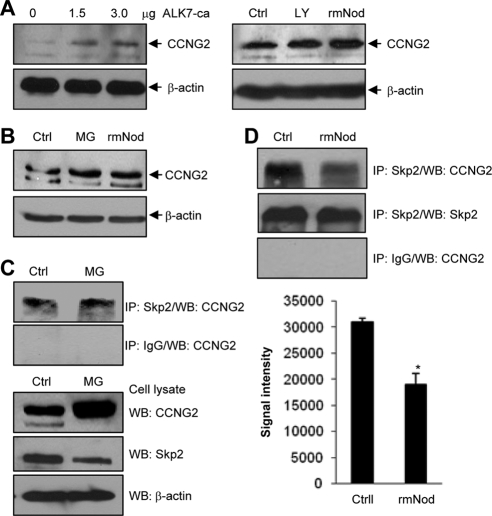
Figure 6.
Regulation of endogenous cyclin G2 level and cyclin G2/Skp2 association. (A) Cyclin G2 expression was induced by ALK7-ca, LY294002 (LY) and rmNodal (rmNod) in OV2008 cells. Cells were transfected with ALK7-ca (0–3 μg) for 6 h followed by 24-h recovery (left panel) or treated with10 μM LY294002 or 500 ng/ml rmNodal (right panel) for 24 h. Ctrl, negative control. (B) MG-132 and rmNodal increased cyclin G2 expression in IOSE-398 cells. Cells were incubated with 500 ng/ml rmNodal or 5 μM MG-132 for 24 h. (C) Detection of endogenous cyclin G2/Skp2 complex. IOSE-398 cells were treated with 5 μM MG-132 or its vehicle control for 24 h, followed by IP using an anti-Skp2 antibody or IgG as a negative control. Cyclin G2 was detected in samples precipitated by the anti-Skp2 antibody, but not in the IgG control samples. Western blots of cell lysates were also performed using anti-cyclin G2, anti-Skp2, and anti-β-actin antibodies. (D) Nodal decreased cyclin G2/Skp2 association. IOSE-397 ells were treated with 500 ng/ml rmNodal or its vehicle control for 24 h, followed by IP using the anti-Skp2 antibody. Cyclin G2 was detected in the anti-Skp2–precipitated samples and the level of cyclin G2/Skp2 complex was lower in the presence of rmNodal (top panel). Skp2 was detected using anti-Skp2 antibody (middle panel). Rabbit IgG was used as a negative control (bottom panel). Graph represents densitometry data of cyclin G2 in anti-Skp2 immunoprecipitated samples (mean±SEM of three experiments). *p<0.05 versus control.