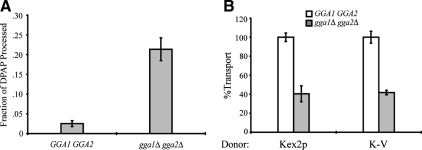
Figure 2.
Deletion of the GGAs results in increased PSHA processing and reduced cell-free transport of Kex2p and K-V. (A) PSHA is cleaved in vivo as a result of gga1 gga2 disruption. MSS samples prepared from JBY209 (kex2Δ GGA1+ GGA2+) and MAY8 (kex2Δ gga1Δ gga2Δ), both transformed with pPSHA, were incubated under transport reaction conditions and then subjected to IP with anti-HA antibody and mock IP in the presence of 1% Triton X-100. Supernatants were assayed for DPAP activity by using Ala-ProAMC (Brickner et al., 2001). The fraction of PSHA cleaved in vivo (i.e., lacking the HA epitopes) is the ratio of DPAP activity in the anti-HA IP to that in the mock IP. (B) Donor MSS were prepared from JBY209 (GGA1+ GGA2+) and MAY4 (gga1Δ gga2Δ) expressing Kex2p or K-V. Acceptor MSS were prepared from JBY209 (GGA1+ GGA2+) expressing PSHA. Cell-free transport reactions were then carried out (20 min at 30°C). Extents of transport observed for controls (GGA1+ GGA2+) were 9.2% JBY209 (Kex2p) and 10.3% JBY209 (K-V), adjusted to 100% in the figure. Experimental values (gga1Δ gga2Δ) are shown as percentage of the control values.