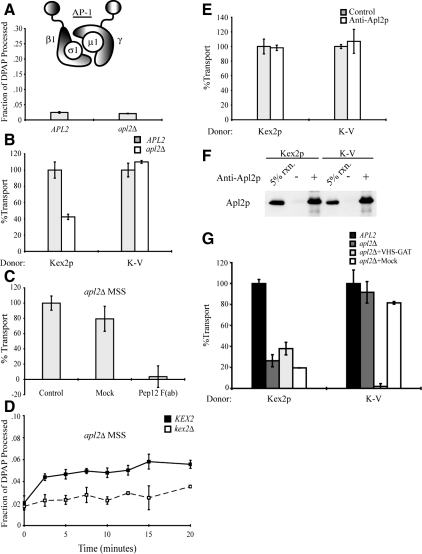
Figure 6.
AP-1 is not required for cell-free TGN-to-PVC transport of Kex2p and K-V, but it is required for localization of Kex2p to the Gga-dependent donor compartment. (A) PSHA is not cleaved in vivo as a result of AP-1 disruption. MSS samples prepared from JBY209 (kex2Δ APL2+) and MAY8 (kex2Δ apl2Δ), both transformed with pPSHA, were incubated under transport reaction conditions then subjected to IP with anti-HA antibody and mock IP in the presence of 1% Triton X-100, and supernatants were assayed for DPAP activity by using Ala-ProAMC (Brickner et al., 2001). The fraction of PSHA cleaved in vivo (i.e., lacking the HA epitopes) is the ratio of DPAP activity in the anti-HA IP to that in the mock IP. (B) MSS were prepared from JBY209 (APL2+) and MAY8 (apl2Δ) expressing Kex2p, K-V, or PSHA. Cell-free transport reactions were then carried out (20 min at 30°C). Extents of transport observed for controls (APL2+) were 10.5% JBY209 (Kex2p), 9.7% JBY209 (K-V), adjusted to 100% in the figure. Experimental values (apl2Δ) are shown as percentage of the control values. (C) Residual Kex2p transport in apl2Δ MSS is dependent on Pep12p. Anti-Pep12p was subjected to papain cleavage to create F(ab) fragments against the cytosolic domain of Pep12p. A mock papain cleavage reaction (Mock) was performed to control for potential papain-dependent inhibition. Kex2p and PSHA MSS from strain MAY8 (apl2Δ) were combined and preincubated with 3.5 μg of anti-Pep12p F(ab), with a mock-purified sample (equivalent volume) or with no addition (control), for 1 h on ice. Cell-free transport reactions were then carried out (20 min at 30°C). Extent of transport observed for control [no Mock or anti-Pep12p F(ab)] was 6.2%, adjusted to 100% in the figure. Experimental values [Mock and anti-Pep12p F(ab)] are shown as percentage of the control values. (D) kex2Δ, KEX2+, or PSHA MSS from strain MAY8 (apl2Δ) were combined and a time course of cell-free transport was then measured as Figure 1C. (E) MSS was prepared from strain JBY209 (APL2) expressing Kex2p, K-V or PSHA. Donor and acceptor MSS samples were combined and preincubated with 14 μg of anti-Apl2p antibody or no antibody (control) for 1 h on ice. Cell-free transport reactions were then carried out (20 min at 30°C). Extents of transport observed for controls (no anti-Apl2p) were 12.4% JBY209 (Kex2p), 11.8% JBY209 (K-V), adjusted to 100% in the figure. Experimental values (+ anti-Apl2p) are shown as percentage of the control values. (F) Affinity-purified anti-Apl2p recognizes Apl2p during the course of the reaction. An aliquot of each reaction shown in E was incubated with protein A-Sepharose for 1 h at 4°C. Protein A-Sepharose pellets were subsequently washed and solubilized in SDS-PAGE sample buffer. Eluted samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Apl2p. (G) Residual Kex2p transport in reactions containing donor and acceptor MSS from MAY8 (apl2Δ) is resistant to inhibition by purified Gga2 VHS-GAT. MSS were prepared from JBY209 (APL2+) and MAY8 (apl2Δ) expressing Kex2p, K-V, or PSHA. Donor and acceptor MSS samples from MAY8 (apl2Δ) were combined and preincubated with 12 μg of purified Gga2p VHS-GAT, with a mock-purified sample (equivalent volume) or with no addition, for 1 h on ice. Donor and acceptor MSS samples from JBY209 (APL2+) were combined and preincubated with no addition (control). Cell-free transport reactions were then carried out (20 min at 30°C). Extents of transport observed for the controls (APL2+, no addition) were 9.9% JBY209 (Kex2p), 10.1% JBY209 (K-V), adjusted to 100% in the figure. Reactions containing MSS from apl2Δ are shown as percentage of the control values.