Figure 1.
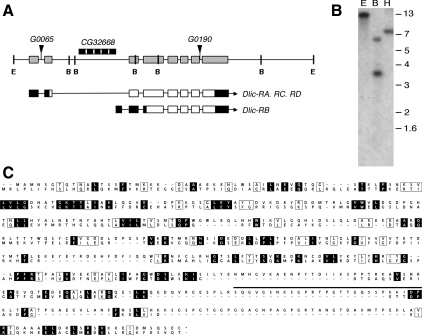
A single gene encodes the Dynein1 Dlic in Drosophila. (A) Schematic shows order of introns (thin bars) and exons (wide bars) of Dlic genomic region. Positions of the P-element insertions are designated by triangles. An unrelated gene, CG32668 (hatched bar), lies within the second intron of Dlic. FlyBase identifies four potential ESTs for Dlic; CG1938-RA, -RC, and -RD correspond to the full-length DLIC protein sequence, and CG1938-RB is proposed to result from alternative splicing and use of an alternative start site, generating a shorter protein. We were unable to detect the shorter transcript. Predicted coding regions of the transcripts are indicated by open bars; noncoding regions by black bars. The relative locations of restriction enzyme sites in the Dlic genomic region are shown: E, EcoRI, B, BamHI. (B) A Southern blot of wild-type Drosophila DNA digested with EcoRI (E), BamHI (B), or HindIII (H) was hybridized with radiolabeled Dlic cDNA. Identical results were obtained under conditions of high or low stringency. All bands recognized correspond to sizes predicted from the sequence of the Dlic gene. (C) Alignment of the predicted peptide sequences of LIC subunits for Dynein 1 (top) and Dynein 2 (below). Identical residues are in shaded boxes, similar residues in open boxes, and gaps are indicated by dashes. The location of the peptide used for antigen production is shown by a bar (___) positioned over the Dynein 1 LIC sequence.