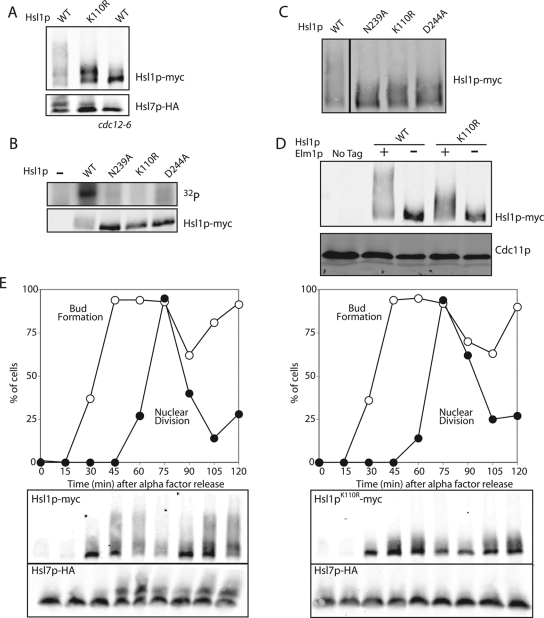
Figure 2.
Hsl1p is regulated by upstream kinases. (A) Catalytically inactive Hsl1p undergoes a partial mobility shift. HSL1-myc HSL7-HA (DLY5000), hsl1K110Rmyc HSL7-HA (DLY5390), and HSL1-myc HSL7-HA cdc12-6 (DLY5336) cells were grown at 24°C to exponential phase and shifted to 37°C for 1 h. Cells were lysed by TCA precipitation and Hsl1p-myc and Hsl7p-HA were detected by Western blotting. (B) Three different mutations in the kinase domain reduce Hsl1p autophosphorylation in vitro. HSL1-myc (DLY8113), hsl1K110Rmyc (DLY8117), hsl1D293Amyc (DLY8116), hsl1N244Amyc (DLY8119), and hsl1Δ (DLY5844) cells were grown to exponential phase at 30°C, harvested, and lysed. Hsl1p was immunoprecipitated and incubated with γ-32P-ATP for 30 min at 30°C before SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Bottom, a Western blot of the proteins used for the kinase assay. (C) The catalytic mutants all display a partial mobility shift. The same strains as in B were lysed by TCA precipitation and Hsl1p-myc was detected by Western blotting. (D) The mobility shift associated with both wild-type Hslp1 and Hsl1pK110R is lost in the absence of Elm1p. Untagged (DLY1), HSL1-myc ELM1 (DLY8113), HSL1-myc elm1Δ (DLY9806), hsl1K110Rmyc ELM1 (DLY8117), and hsl1K110Rmyc elm1Δ (DLY9803) cells were grown to exponential phase at 30°C and lysed by TCA precipitation, and Hsl1p-myc was detected by Western blotting. Cdc11p (septin) was used as a loading control. (E) The mobility shift of catalytically inactive Hsl1p occurs at the time of bud emergence. HSL1-myc HSL7-HA (DLY5000) and hsl1K110Rmyc HSL7-HA (DLY5390) cells were synchronized in G1 with α-factor and released into fresh media at 30°C. The % of cells that had budded or undergone nuclear division were scored at the indicated times after release (n = 100 cells scored from DAPI-stained samples). Cells were lysed by TCA precipitation and Hsl1p-myc and Hsl7p-HA were detected by Western blotting.