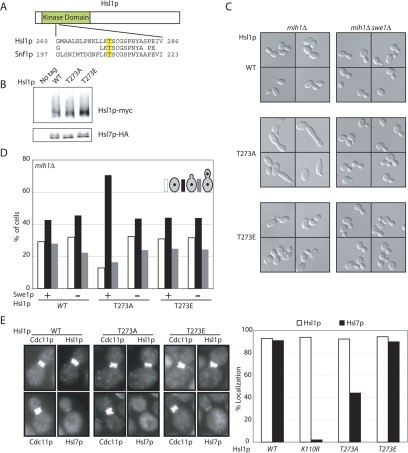
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation of Hsl1p T273 is important for Hsl1p function. (A) Alignment of Snf1p and Hsl1p activation loop sequences. (B) Hsl1p, Hsl1pT273A, and Hsl1pT273E are expressed at similar levels in vivo. Untagged (DLY1), HSL1-myc HSL7-HA (DLY8113), hsl1T273Amyc HSL7-HA (DLY7841), and HSL1T273Emyc HSL7-HA (DLY10072) cells were grown to exponential phase at 30°C, lysed by TCA precipitation, and Hsl1p-myc, and Hsl7p-HA were detected by Western blotting. (C) Hsl1pT273A is less biologically active than Hsl1p or Hsl1pT273E. HSL1-myc mih1Δ (DLY9882), HSL1T273Emyc mih1Δ (DLY 11005), hsl1T273Amyc mih1Δ (DLY7980), HSL1-myc mih1Δ swe1Δ (DLY9883), HSL1T273Emyc mih1Δ swe1Δ (DLY 11006), and hsl1T273Amyc mih1Δ swe1Δ (DLY11007) cells were grown to exponential phase at 30°C and examined by DIC microscopy. (D) Cell cycle profiles of the cells from C were determined by scoring the budding and nuclear division status of DAPI-stained cells (n = 250). (E) Hsl1pT273A is localized to the bud neck, but does not effectively recruit Hsl7p. HSL1-myc HSL7-HA (DLY8113), hsl1T273Amyc HSL7-HA (DLY7841), HSL1T273Emyc HSL7-HA (DLY7451), and hsl1K110Rmyc HSL7-HA (DLY8117) cells were grown to exponential phase at 30°C and processed for immunofluorescence to visualize the septin Cdc11p together with either Hsl1p-myc (top pairs) or Hsl7p-HA (bottom pairs). Representative cells are shown (left) together with the results of scoring 250 cells with a septin collar for the presence of detectable Hsl1p or Hsl7p (right).