Figure 5.
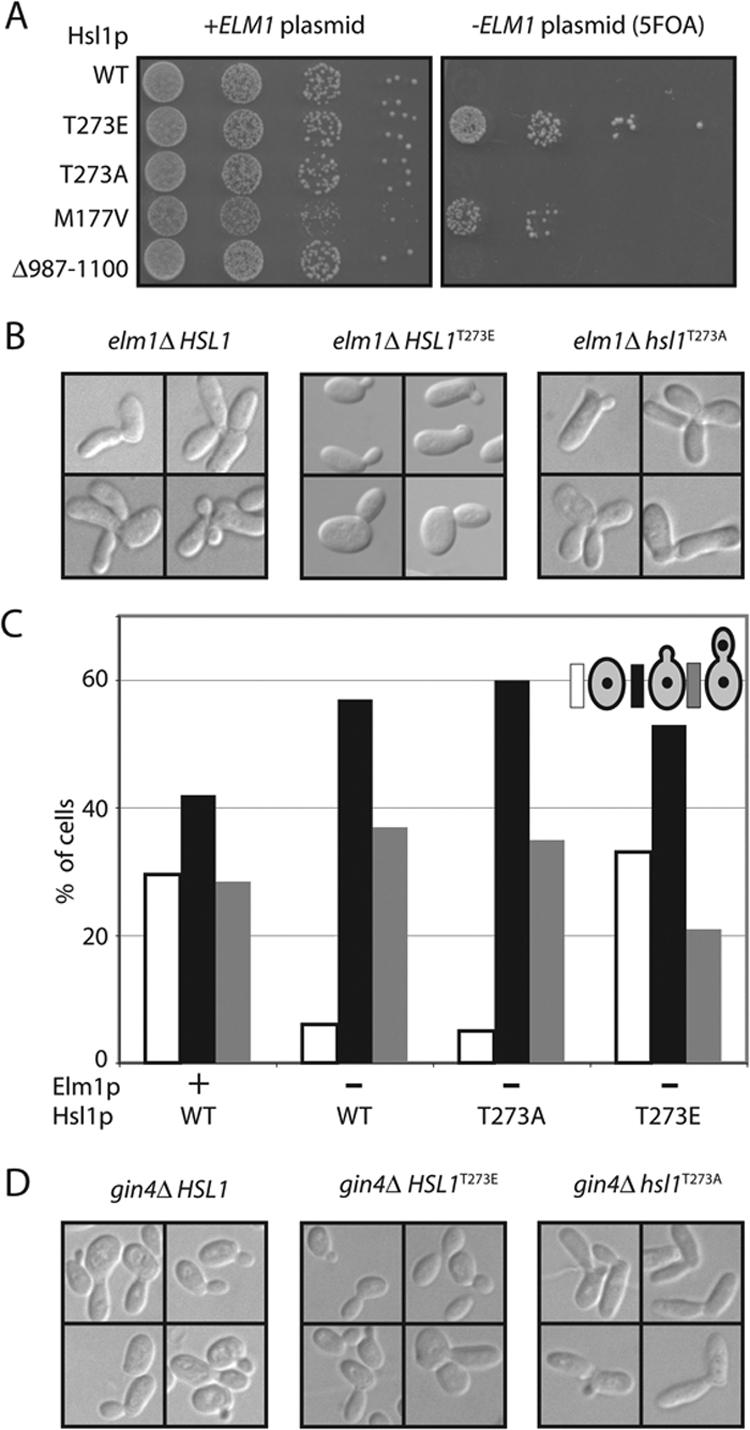
Pseudophosphorylation of Hsl1p T273 suppresses mih1Δ elm1Δ synthetic lethality. (A) A mih1Δ elm1Δ strain kept alive with a URA3-marked plasmid carrying ELM1 was transformed with plasmids expressing the indicated allele of Hsl1p. On 5-FOA media only cells that have lost the ELM1 plasmid can live. Strains: HSL1 (DLY9409), hsl1T273A (DLY9406), HSL1T273E (DLY9407), HSL1M177V (DLY9410), and HSL1Δ987–1100 (DLY9691). Cells were spotted onto YEPD with and without 5-FOA. (B) elm1Δ elongated cell morphology is suppressed by Hsl1pT273E. DIC images of representative cells from proliferating asynchronous cultures of elm1Δ (DLY7704), hsl1T273A elm1Δ (DLY9820), and HSL1T273E elm1Δ (DLY10077) strains. (C) The G2/M cell cycle delay in elm1Δ cells is suppressed by Hsl1pT273E. Cell cycle profiles were determined as described in Figure 3D for the following strains: WT (DLY8113), elm1Δ (DLY9806), hsl1T273A elm1Δ (DLY9820), and HSL1T273E elm1Δ (DLY10077). (D) gin4Δ elongated bud morphology is not suppressed by Hsl1pT273E, but is exacerbated by Hsl1pT273A. DIC images of representative cells from proliferating asynchronous cultures of gin4Δ (DLY4410), hsl1T273A gin4Δ (DLY10076), and HSL1T273E gin4Δ (DLY11008), strains.
