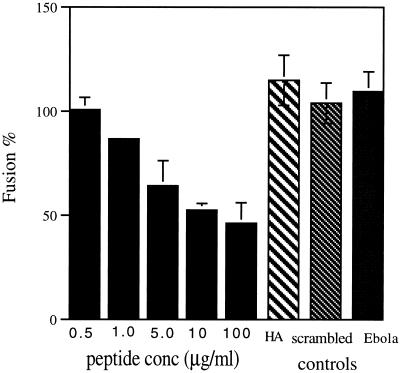
Figure 4.
Fusion inhibition by the GP64 peptide. The effect of various concentrations of GP64 peptide present during the fusion of PKH26 membrane dye–labeled RBCs and stably transfected gp64-expressing Sf9 cells (Ac5 cell line) was determined by dye transfer assay. Controls to evaluate the specificity of the GP64 peptide’s effect were performed as follows. (HA) The GP64 peptide’s (10 μg/ml) effect on HA-mediated cell-to-cell fusion was evaluated with the use of transiently transfected Sf9 cells. (scrambled) A scrambled GP64 leucine zipper peptide (EMLQINLEMEDLHAHIMELNYKNMKILHD) of the same peptide composition but alternative sequence was tested for inhibition of GP64-mediated cell-to-cell fusion activity of transiently transfected Sf9 cells by membrane dye transfer at 10 μg/ml peptide. (Ebola) The GP leucine zipper peptide (GLMHNQDGLICGLRQLANETTQALQLFLRA) was tested for inhibition of GP64-mediated cell-to-cell fusion activity of transiently transfected Sf9 cells by membrane dye transfer at 10 μg/ml peptide. For all experiments, fusion was initiated by application of PBS, pH 5.0, and the extent of fusion was determined by counting fluorescently labeled Sf9 cells (fusion event) and dividing by the sum of PKH26-labeled RBCs in contact with Sf9 cells and fluorescently labeled Sf9 cells. Values represent the means from three separate experiments normalized to wild-type GP64-expressing (100%) or HA-expressing (100%) cells in the absence of peptide. All peptides were present before, during, and after induction of membrane fusion. Error bars represent SE.