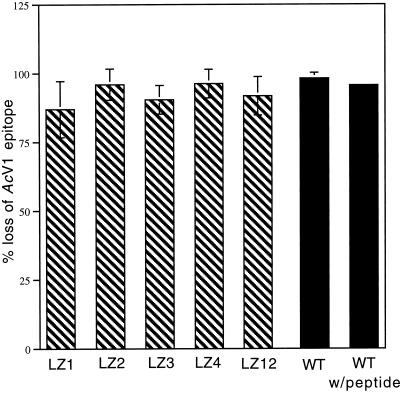
Figure 6.
Conformational changes of wild-type GP64 during peptide inhibition and fusion-defective mutants. The effect of the inhibitory peptide on the initiation of wild-type GP64 pH-induced conformational changes and the ability of leucine zipper mutants LZ1, LZ2, LZ3, LZ4, and LZ12 to undergo pH-induced conformational changes was assessed by cELISA. Black bars represent the percent change (loss) of wild-type (WT) GP64 immunoreactivity with the conformationally sensitive AcV1 antibody in the presence and absence of 100 μg/ml GP64 peptide compared with the wild-type untreated (neutral pH) value. Hatched bars represent the percent change (loss) of mutant immunoreactivity with the conformationally sensitive AcV1 antibody compared with the neutral pH value of each mutant. All results shown are from three separate trials. Error bars represent SE. Because citrate buffer, pH 4.8, rather than PBS, pH 5.0, was used for low pH application, peptide inhibition of membrane fusion with 100 μg/ml GP64 peptide and citrate buffer, pH 4.8, was measured. Results (48% of nonpeptide control) were comparable to those observed with PBS, pH 5.0.