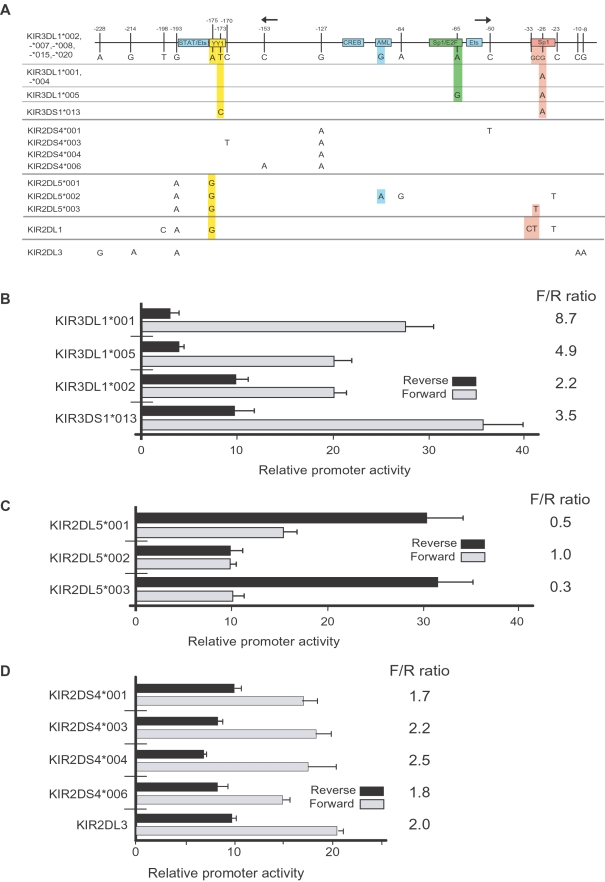
Figure 2. Impact of polymorphisms present in the KIR3DL1, KIR2DS4, KIR2DL3, and KIR2DL5 genes on promoter activity.
(A) A schematic of the KIR bi-directional promoter region is shown with the position of transcription factor binding sites indicated by labeled boxes. The sites of transcript initiation for the sense and antisense promoters are shown by the rightward and leftward arrows respectively. The vertical lines indicate the positions of polymorphic nucleotides relative to the KIR3DL1*002 allele. Numbers above the lines indicate the positions of the polymorphic residues relative to the start codon of the KIR3DL1 gene. The nucleotide present at each variable position is shown for the KIR3DL1*002 gene and only differences are shown for the remaining alleles. (B) The promoter activities of KIR3DL1/S1 promoter alleles are shown. The 229 bp core promoter region of the KIR3DL1 alleles and KIR3DS1 were cloned into the pGL3 reporter vector in the forward and reverse orientation, and the promoter activity of each construct was determined by transfection into the YT-Indy human NK cell line. The ratio of forward promoter activity to reverse activity (F/R ratio) is listed for each allele. (C) Promoter activities of KIR2DL5 alleles. (D) Characterization of promoter activity of the KIR2DS4 alleles and the KIR2DL3 promoter. Values represent fold increase of luciferase activity relative to empty pGL3 vector. The mean and SD of at least 3 independent experiments are shown.