Fig. 1.
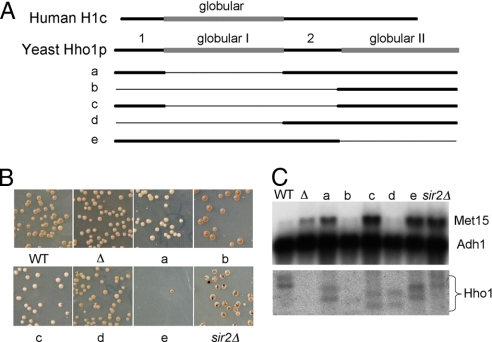
An HHO1 disruption results in increased MET15 expression. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating hho1 deletions a-e. Human H1c is drawn as a reference (drawn to scale). (B) Mutant and wild-type strains were plated on Pb+ indicator plates. The lighter the color of the colony, the more MET15 expression, and the lower the presumed rDNA compaction. Sectors resulting from homologous recombination in the rDNA and loss of the MET15 gene are most numerous in the sir2Δ strain (JS218). Colonies were plated at 30°C for 5 days and then at 4°C for 1 additional week before photography. (C) Northern blot monitoring the expression of MET15 in the different mutants of Hho1 and sir2. Fragments of MET15 and ADH1 were used simultaneously as probes. Identical amounts of total cell RNA were loaded in each lane. A parallel gel (shown below) was probed with an Hho1 fragment. There are consistently two different-sized transcripts for Hho1. The differing sizes of the Hho1 transcripts in the different lanes correspond to the deletions made in the Hho1 gene by the mutagenesis. The hho1Δ deletion strain shows no hho1 transcript. Quantitation of the transcripts, normalized to the Adh1 probe, is presented in Table S1).