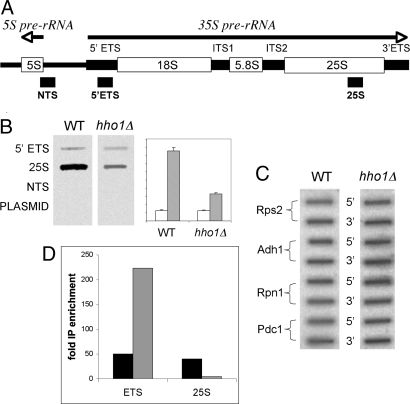
Fig. 2.
Pol I processivity is defective in the hho1Δ mutant. Run-on transcription was performed as described in Methods. (A) Schematic diagram of the rDNA transcription unit. RNA polymerase I transcribes the 35S primary rRNA transcript. DNA sequences serving as probes in B and corresponding to the indicated segments of the nontranscribed spacer (NTS), the 5′ external transcribed spacer (5′ ETS), and the 25S rRNA are indicated. (B) Slot blot hybridization of the probes described in A with labeled RNA from wild-type and hho1Δ cells. Quantitation of two separate experiments with standard deviation bars on right (arbitrary abscissa units). Open and stippled bars represent ETS and 25S probes, respectively. (C) Slot blot hybridization of PCR amplified DNA fragments from 5′ and 3′ ends of genes transcribed by pol II. Primers are listed in Table S3. (D) Quantitation of ChIP experiment verifying defective RNA pol I processivity in hho1Δ. cross-linked, HA-tagged RNA pol I was immunoprecipitated from wild type and hho1Δ cells together with associated DNA. After cross-link reversal, quantitative PCR of ETS and 25S rDNA sequences were performed. Black and stippled bars represent enrichment of the DNA sequences relative to input DNA precipitated from wild-type and hho1Δ extracts, respectively.