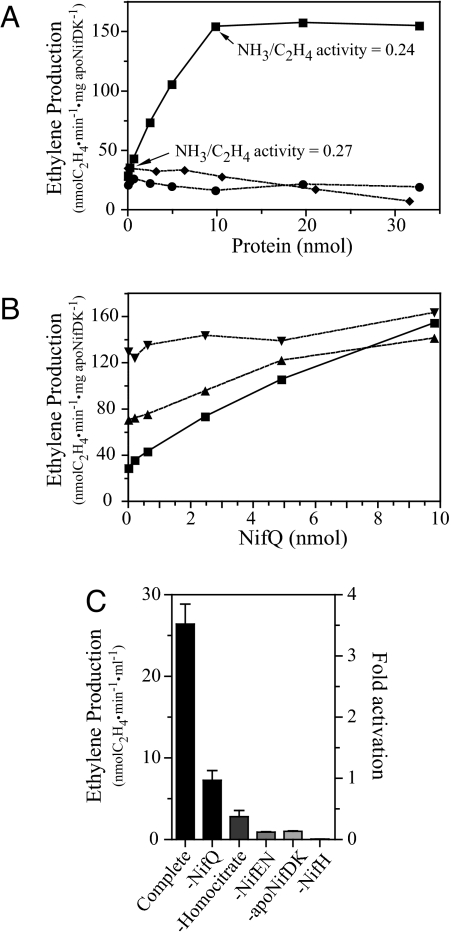
Fig. 4.
NifQ serves as a molybdenum donor for in vitro synthesis of FeMo-co with purified components. FeMo-co synthesis was determined by the acetylene reduction activity of matured NifDK. In addition, the dinitrogen reduction activity of matured NifDK was determined in selected samples. All vials were acid-washed and thoroughly rinsed with Milli-Q water to remove traces of molybdenum. FeMo-co synthesis reactions contained 0.43 nmol of apo-NifDK, 0.48 nmol of VK-cluster loaded NifEN, 2.4 nmol NifH, and the indicated amount of NifQ (0–30 nmol). (A) Titration of FeMo-co synthesis reactions with increasing amounts of purified NifQ (squares), purified rNifQ (circles), or purified cyanobacterial nitrate reductase (NarB) (diamonds). No molybdate was added to the reactions. (B) Titration of FeMo-co synthesis reactions with increasing amounts of purified NifQ in the presence of 18 μM molybdate (inverted triangles), 0.18 μM molybdate (triangles), or no molybdate (squares). (C) Requirement for different components in the FeMo-co synthesis reaction with purified proteins. No molybdate was added to the reactions. All reactions contained 4.9 nmol of NifQ except the reaction lacking NifQ. Fold activation with respect to the reaction lacking NifQ is indicated in the right y axis. In the experiments lacking NifH, FeMo-co synthesis was stopped by the addition of 0.3 mM (NH4)2MoS4 before assaying the activity of reconstituted NifDK. Data are the average of two to four independent determinations.