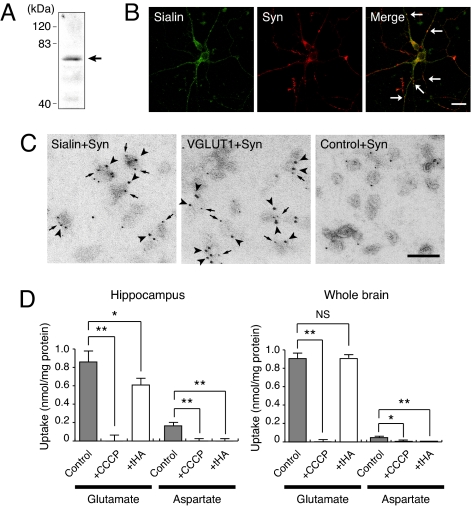
Fig. 2.
ATP-dependent uptake of aspartate was detected in sialin-containing synaptic vesicle preparation from hippocampus. (A) Immunoblotting revealed the presence of sialin in the hippocampal P2 fraction. The position of sialin is marked by an arrow. (B) Sialin is partially colocalized with synaptophysin. Cultured hippocampal neurons were double immunostained with antibodies against sialin and synaptophysin. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (C) Double-labeling immunoelectron microscopy demonstrated the association of sialin with synaptophysin-containing vesicles. Samples were treated with sets of anti-synaptophysin monoclonal antibodies (5-nm particles, arrows) and anti-sialin serum (10-nm particles, arrowheads), anti-synaptophysin monoclonal antibodies (5-nm particles, arrows) and anti-VGLUT1 serum (10-nm particles, arrowheads), or anti-synaptophysin monoclonal antibodies (5-nm particles) and control serum (10-nm particles). (Scale bar, 100 nm.) (D) ATP-dependent uptake of aspartate and glutamate at 5 min by P2 fractions isolated from hippocampus and whole brain. Concentrations of CCCP and tHA were 1 μM and 5 mM, respectively.