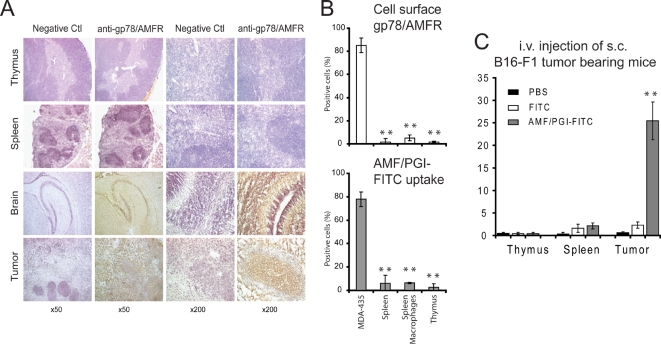
Figure 7. Gp78/AMFR expression and AMF/PGI uptake in normal mouse immune tissue and cells.
A. Immunohistochemical labeling of tissue sections showed no gp78/AMFR reactivity in normal mouse spleen and thymus. However, strong positive gp78/AMFR staining was detected in 5 day old mouse brain tissue and in 20 day old HCT116 s.c. tumor sections. A representative experiment of eight is shown (original magnification, ×50 and ×200). B. Cell surface gp78/AMFR expression (top panel) and AMF/PGI-FITC uptake (bottom panel) of single cell suspensions prepared from mouse spleen and thymus, an enriched population of spleen macrophages as well as MDA-435 cells were assessed by flow cytometry and the percentage of positive cells is presented. The data represent the average of three separate experiments (mean±SEM; **, P≤0.001).). C. B16-F1 melanoma tumors were established s.c. in C57/BL6 mice and after 12 days, mice were injected i.v. with PBS, 250 µg/ml AMF/PGI-FITC or an equivalent concentration of free FITC. After two hours, spleen, thymus and B16-F1 s.c. tumors were mechanically dissociated, treated with pronase and analyzed for FITC positivity by flow cytometry. The data represent the average of six different tumors (mean±SEM; **, P≤0.001, relative to PBS injected mice).