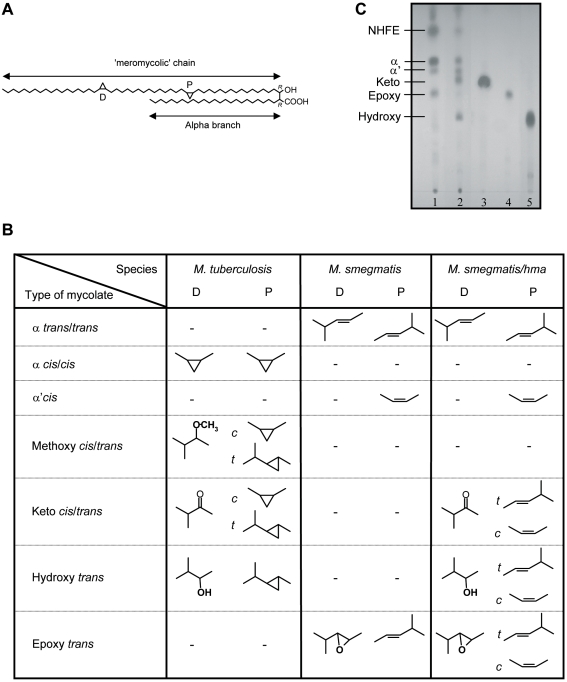
Figure 3. Structure of the mycolic acids found in M.tb, M. smegmatis and M. smegmatis/hma respectively.
A) Dicyclopropanated mycolic acid (α-mycolate) from M. tuberculosis. The chemical functions introduced by methyltransferases occur at the proximal (P) and distal (D) positions. B) TLC profile of the mycolic acid methyl esters from: lane1, M. smegmatis; lane 2, M. smegmatis/hma; lane 3, ketomycolate; lane 4, epoxymycolate; lane 5, hydromycolate. NHFE, non-hydroxylated fatty esters. C) Types of functional groups present at both the proximal and distal positions of the different species of mycolates found in M. tuberculosis, M. smegmatis and M. smegmatis/hma.