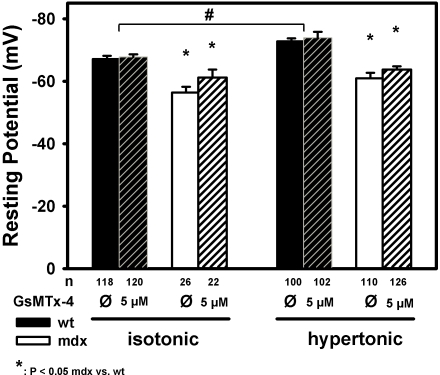
Figure 9. Mechanosensitive channel activity during osmotic challenge does not induce marked membrane depolarisations in mdx fibres.
Resting membrane potentials in many intact fibres were recorded by repetitive impalement of whole interossei muscles from wt (black) and mdx (white) mice without enzymatic treatment under isotonic and hypertonic conditions. The contribution of cation influx through mechanosensitive channels to the resting potential when muscles were immersed in either isotonic or hypertonic Ringer solution was assessed by pre-incubation with 5 µM of the spider peptide GsMTx-4, a selective MsC blocker. Although potentials were more depolarised in mdx fibres already under isotonic conditions, this did not increase under hypertonic conditions, nor was there a marked contribution from MsC to depolarisation. n: number of individual potential recording.