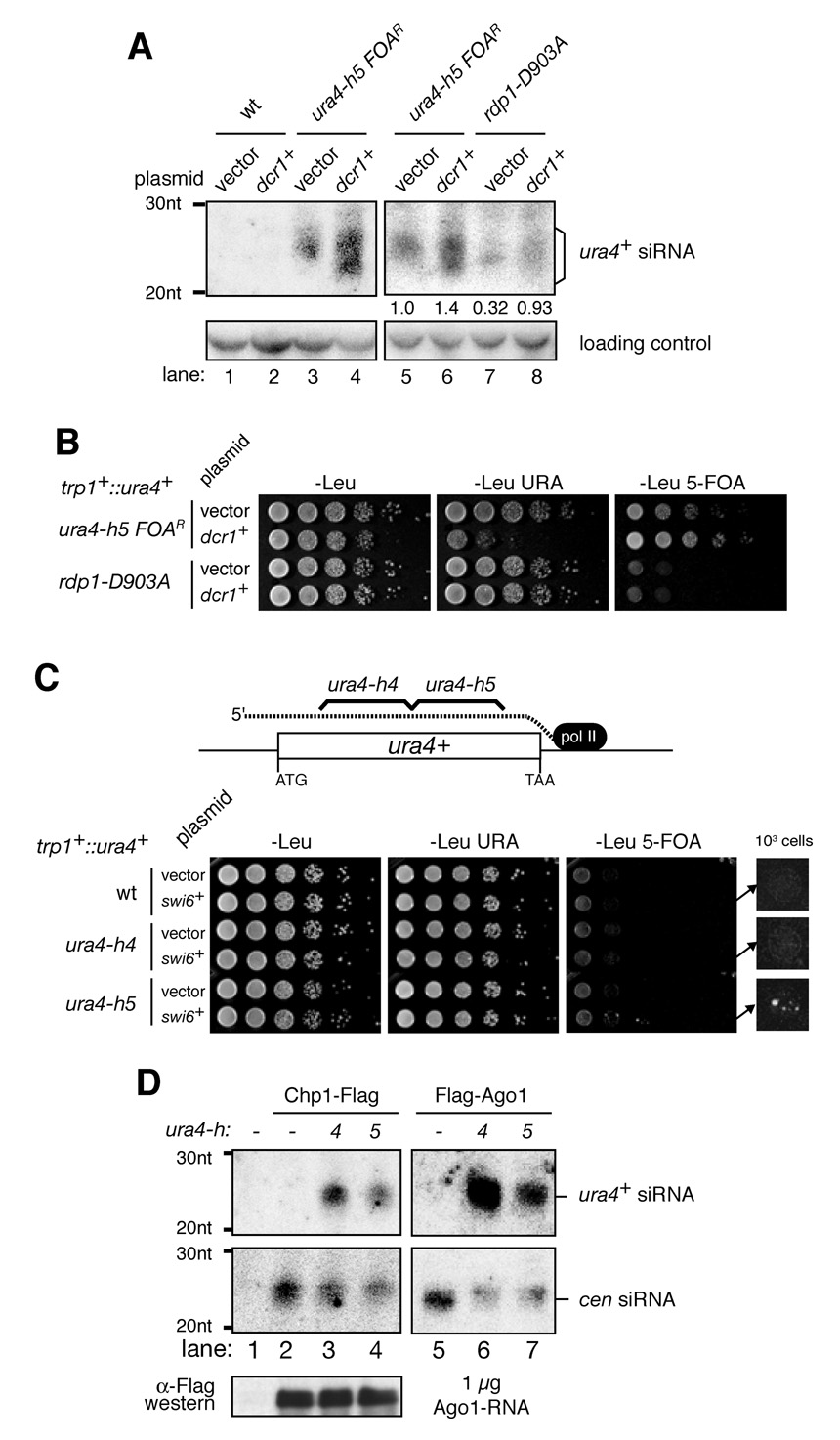
Figure 6. Rdp1 catalytic activity and location of siRNA target sequences control hairpin-induced silencing.
A, Overexpression of Dcr1 boosted hairpin siRNA levels in both rdp1+ and rdp1-D903A cells. B, Dcr1 overexpression did not circumvent the requirement for Rdp1 catalytic activity but increased the efficiency of hairpin-induced silencing of trp1+::ura4+ in rdp1+ cells. C, In contrast to the ura4-h5 hairpin, a ura4-h4 hairpin, which targets the 5’ half of the ura4+ transcript did not promote trp1+::ura4+ silencing. trp1+::ura4+ cells with ura4-h4 or -h5 were tested by Swi6 overexpression as described in Figure 3A. Diagram indicates the regions of ura4+ targeted by each hairpin. D, Northern blots of pull-down assays showing that siRNAs produced by both ura4-h4 and ura4-h5 were loaded onto Ago1 and the RITS complex. Centromeric (cen) siRNAs served as controls.