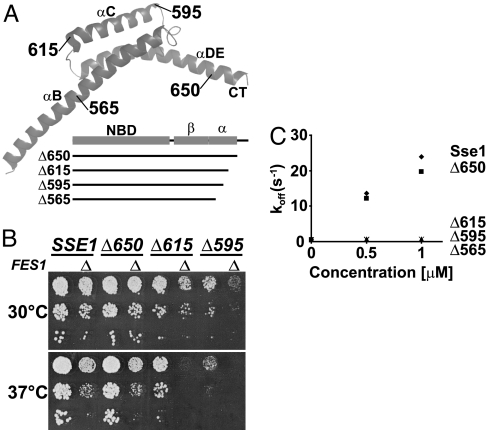
Fig. 3.
The α-helical SBD subdomain is important for the interaction with Ssa1. (A) Schematic representation of the truncation mutants of Sse1. The α-helical subdomain (α) is drawn as a ribbon structure (13) with names of helices and the last residue of each truncation mutant indicated. (B) Ten-fold serial dilutions of sse1Δ sse2Δ or sse1Δ sse2Δ fes1Δ (Δ) yeast strains carrying SSE1, or derived truncated alleles, in the context of its endogenous locus on a single-copy plasmid were spotted onto YPD medium and incubated at 30 °C or 37 °C for 2 days. (C) MABA-ADP dissociation rate [koff (s−1)] from Ssa1 (0.5 μM) by the indicated concentrations of Sse1 or derived truncation mutants. The Sse1 proteins were preincubated with 3 mM ATP before measuring the release rates with a stopped-flow instrument.