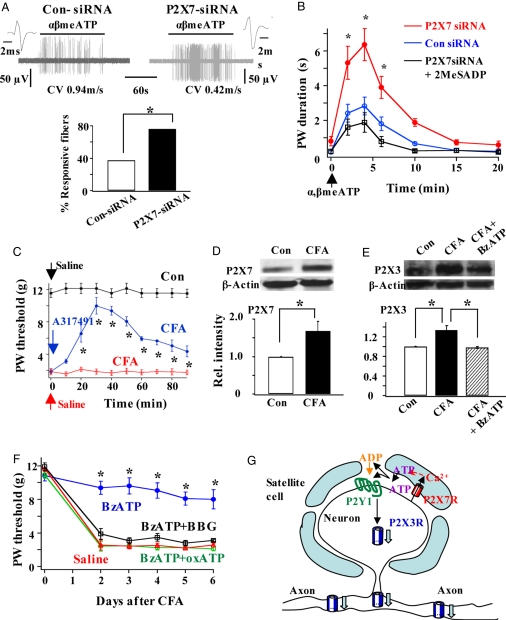
Fig. 4.
Functional significance of the inhibitory control of P2X3R expression by P2X7Rs. (A) The percentage of fibers responding to α,β-meATP increased in P2X7-siRNA rats. (Upper) Examples of the activity of fibers isolated from a skin-nerve preparation of a control siRNA rat and of a P2X7R-siRNA rat. (Lower) In 5 of 13 cases (38.4%) Aδ and C fibers recorded in skin-nerve preparations isolated from control siRNA rats responded to α,β-meATP. A much higher percentage of fibers (16 of 21; 76.2%) isolated from P2X7-siRNA rats were sensitive to α,β-meATP (χ2 test, *P < 0.05). (B) Flinch behavioral responses to α,β-meATP were much enhanced in P2X7-siRNA rats. The enhanced responses were reversed in rats treated with intrathecal P2X7-siRNA + 2MeSADP (n = 4–7; ANOVA, *P < 0.05). (C) CFA-produced allodynia was P2X3R-mediated. Compared with the PBS solution-injected rats, the paw withdrawal threshold to von Frey stimulation in CFA rats was much reduced. The allodynia in CFA rats was reversed when the P2X3R activation was blocked by an intraplantar injection of the P2X3R antagonist A317491 (6 mM, 50 μl) into the tested paw (*P < 0.05 vs. CFA rat group; n = 5). Arrows indicate the time of saline solution or A317491 injection. (D) P2X7R expression was enhanced in rats inflamed with CFA (P2X7: CFA/control = 1.68 ± 0.26, n = 9, *P < 0.05). (E) Although P2X3R expression was higher after inflammation (CFA/control = 1.34 ± 0.09, n = 3, *P < 0.05), P2X3R expression in CFA + BzATP rats was not different from that in control rats ([CFA + BzATP]/control = 0.98 ± 0.02, n = 3, P > 0.05). (F) Activation of P2X7R by pretreatment of rats with BzATP effectively blocked the development of CFA-induced allodynia. When the P2X7R activation was blocked by BBG or oxATP, BzATP could no longer prevent the development of allodynia. Six animals were tested in each rat group (*P < 0.05 vs. saline solution, BzATP + BBG or BzATP + oxATP rat group). (G) The proposed P2X7R–P2Y1R–P2X3R inhibitory control results in a decrease in P2X3Rs at afferent terminals and thus a reduction in nociception.