Figure 2.
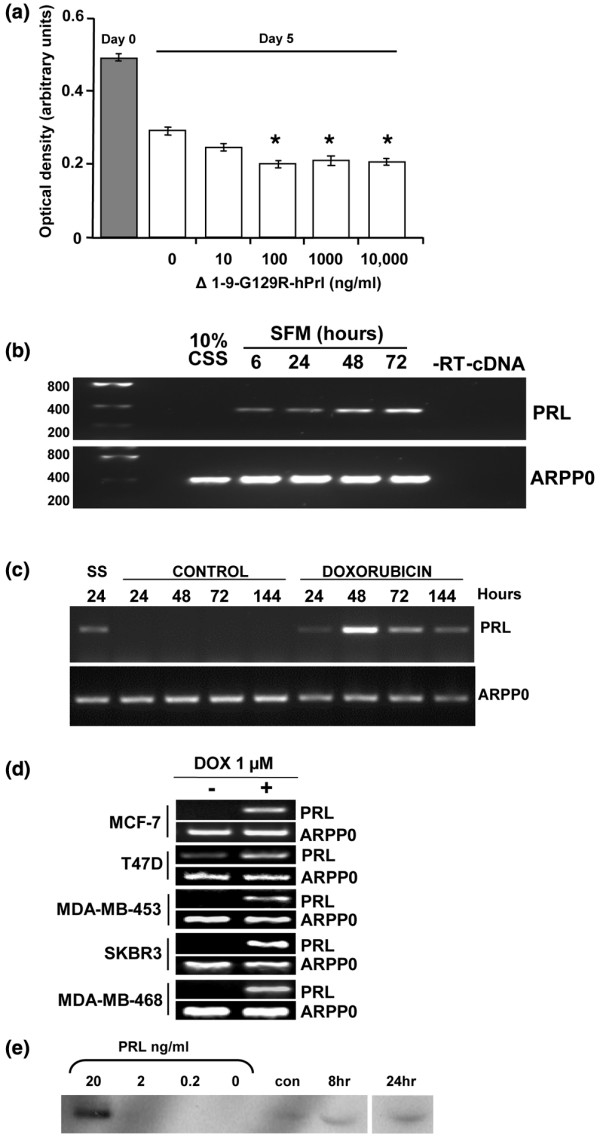
Autocrine prolactin production is stimulated by serum starvation and treatment with doxorubicin. (a) Monolayer culture of MCF-7 cells in serum-free medium over 5 days (open bars) resulted in cell loss compared with the cell number at 24 hours after plating in 10% charcoal stripped serum (CSS) (grey bar). Δ1–9-G129R-hPrl (Δ1–9) increased cell loss in a dose-dependent manner (clear bars). Prolactin (PRL) mRNA was detected in MCF-7 cells by RT-PCR in response to (b) serum starvation and (c) treatment with 1 μM doxorubicin for 24 hours, but not in cells grown in control medium (10% CSS). ARPP0, acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P0; SFM, serum free medium. Following doxorubicin treatment for 24 hours, cultures were washed and fresh control medium was added. Times correspond to the number of hours from the start of the experiment. (d) All five cell lines were treated with doxorubicin (DOX) as in (c) and were harvested at 48 hours, and they demonstrate the induction of prolactin mRNA expression. ARPP0 was used as a housekeeping gene loading control in all RT-PCR experiments. (e) Western analysis of prolactin in cell culture media. Bracketed lanes represent the positive control concentration curve of recombinant human prolactin. Other lanes are conditioned media from MCF-7 cells in 10% CSS alone (con) or following 1 μM doxorubicin treatment for 8 and 24 hours and conditioned media harvested 48 hours after the start of the experiment.
