Abstract
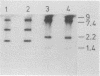
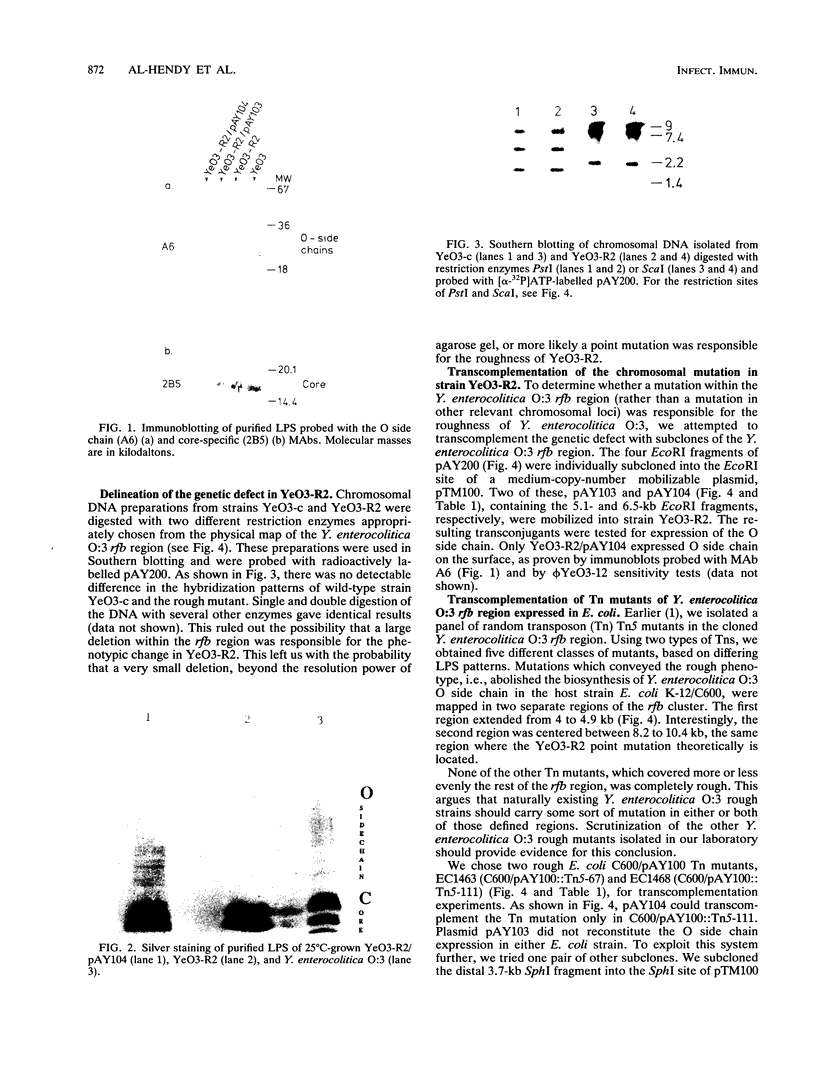
The rfb gene cluster of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3, responsible for the biosynthesis of the O side chain, was previously cloned, and a Y. enterocolitica O:3 side chain-specific bacteriophage (phi YeO3-12) was isolated (A. Al-Hendy, P. Toivanen, and M. Skurnik, Microb. Pathog. 10:47-59, 1991). This paper describes the isolation and characterization of the bacteriophage phi YeO3-12-resistant mutant of Y. enterocolitica O:3, YeO3-R2. Lipopolysaccharide isolated from YeO3-R2 lacked the O side chain, as evidenced by silver staining and by immunoblots probed with a Y. enterocolitica O:3 O side chain-specific monoclonal antibody. The core was complete, as shown in immunoblots probed with an outer core-specific monoclonal antibody. In Southern blotting with the cloned Y. enterocolitica O:3 rfb region as a probe, there was no detectable difference in the hybridization pattern of chromosomal DNA isolated from YeO3-R2 and that isolated from wild-type Y. enterocolitica O:3. This suggests that a point mutation, rather than a large deletion, was responsible for the rough phenotype of YeO3-R2. The virulence of YeO3-R2 was determined in an orally infected desferal-attenuated murine model. The mutant was approximately 50-fold less virulent than the isogenic wild type. The ability of YeO3-R2 to reexpress O side chain, and hence full virulence, was reconstituted by complementing the chromosomal mutation in trans with the distal 6.5 kb of the Y. enterocolitica O:3 rfb region. This same 6.5-kb fragment transcomplemented a transposon mutation in the same area of the Y. enterocolitica O:3 rfb region when expressed in Escherichia coli. This transcomplementation implies that the rfb region of Y. enterocolitica O:3 is organized into at least two separate operons.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binns M. M., Vaughan S., Timmis K. N. 'O'-antigens are essential virulence factors of Shigella sonnei and Shigella dysenteriae 1. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985 Jun;181(1-2):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Factors promoting acute and chronic diseases caused by yersiniae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jul;4(3):309–324. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Row B., Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R. Conversion of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 to phage type 7 involves loss of lipopolysaccharide with concomitant loss of virulence. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conchas R. F., Carniel E. A highly efficient electroporation system for transformation of Yersinia. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90505-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delor I., Kaeckenbeeck A., Wauters G., Cornelis G. R. Nucleotide sequence of yst, the Yersinia enterocolitica gene encoding the heat-stable enterotoxin, and prevalence of the gene among pathogenic and nonpathogenic yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2983–2988. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2983-2988.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Endert J., Kamps M. A., van Boven C. P. Role of lipopolysaccharide in opsonization and phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):182–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.182-189.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Ogasawara M., Hill J. L., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Toivanen A., Yu D. T. Analysis of IgA antibodies to lipopolysaccharide in Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1142–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. M., Neal B., Santiago F., Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Structure and sequence of the rfb (O antigen) gene cluster of Salmonella serovar typhimurium (strain LT2). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):695–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Otsuki K., Tsubokura M. Growth temperature-dependent variation in the bacteriophage-inactivating capacity and antigenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica lipopolysaccharide. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2739–2747. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marolda C. L., Welsh J., Dafoe L., Valvano M. A. Genetic analysis of the O7-polysaccharide biosynthesis region from the Escherichia coli O7:K1 strain VW187. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3590–3599. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3590-3599.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Hovi M., Saxén H., Valtonen M., Valtonen V. Salmonella, complement and mouse macrophages. Immunol Lett. 1988 Nov;19(3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nagai T., Nakaya R., Kondo S., Murakami M., Hisatsune K. HeLa cell invasiveness and O antigen of Shigella flexneri as separate and prerequisite attributes of virulence to evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekkola-Heino K., Viljanen M. K., Ståhlberg T. H., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Monoclonal antibodies reacting selectively with core and O-polysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1987 Feb;95(1):27–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson D. E., Falkow S. Nonpathogenic isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica do not contain functional inv-homologous sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1059–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1059-1064.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Selective pressures and lipopolysaccharide subunits as determinants of resistance of clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):320–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.320-328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUBBAIAH T. V., STOCKER B. A. ROUGH MUTANTS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. I. GENETICS. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2011298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Lack of correlation between the presence of plasmids and fimbriae in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;56(3):355–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvano M. A., Crosa J. H. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of chromosomal genes determining the O7 lipopolysaccharide antigen of a human invasive strain of E. coli O7:K1. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.937-943.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Brade V. Influence of surface modulations by enzymes and monoclonal antibodies on alternative complement pathway activation by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1984–1989. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1984-1989.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. M., Manning P. A. Mapping of chromosomal loci associated with lipopolysaccharide synthesis and serotype specificity in Vibrio cholerae 01 by transposon mutagenesis using Tn5 and Tn2680. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00331294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Hendy A., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. Expression cloning of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 rfb gene cluster in Escherichia coli K12. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jan;10(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90065-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Hendy A., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. Rapid method for isolation and staining of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(4):331–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Hendy A., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. The effect of growth temperature on the biosynthesis of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 lipopolysaccharide: temperature regulates the transcription of the rfb but not of the rfa region. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jan;10(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90068-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]