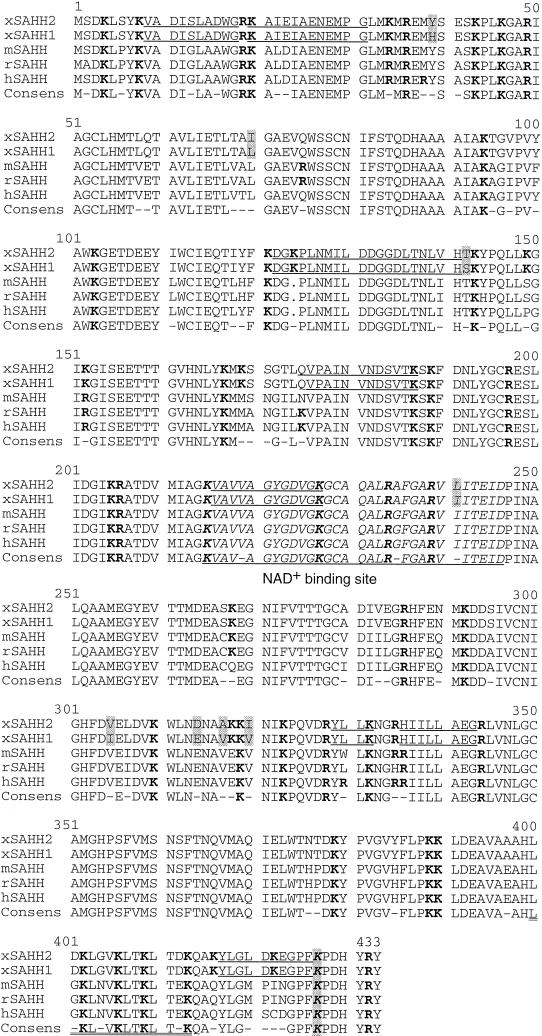
Figure 1.
Protein sequence alignment of vertebrate SAHH. The cDNA-derived amino acid sequences of X. laevis (xSAHH 1, GenBank accession number [gb] L35559 and this communication; xSAHH 2, gb AJ007835 and this communication), mouse (mSAHH, gb L32836), rat (rSAHH, gb M15185) and human (hSAHH, gb M61832) have been aligned together with the consensus sequence, using the GCG programs Pileup and Pretty. The two isoforms of X. laevis are distinguished from one another by eight conservative changes, each marked by shading. Sequences obtained by protein microsequencing of tryptic peptides of the X. laevis oocyte protein are underlined in xSAHH. Lysine and arginine residues are shown in bold. The NAD+ binding site is printed in italics and underlined in the consensus. An amphiphatic helical domain near the C terminus is underlined twice, and a lysine residue (K427) shown to be essential for tetramer formation and for catalytic activity of the hSAHH (Ault-Riche et al., 1994) is printed in italics and shaded.