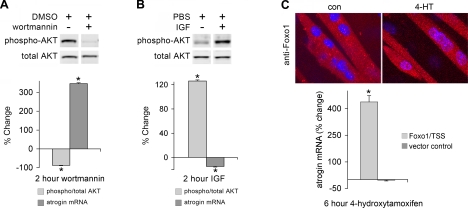
Fig. 3.
Canonical AKT pathway regulation of atrogin. C2C12 myotubes were treated with wortmannin 100 nm (A), IGF 10 ng/ml (B) for 2 h, or subjected to overexpression of a Foxo1/TSS mutant resistant to inhibition by AKT (C). This mutant is fused to the ligand-binding domain of the estrogen receptor and was induced to translocate to the nucleus with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HT, 1 μM). AKT was measured by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for total and phospho-AKT. AKT phosphorylation decreased with wortmannin and increased with IGF (*P < 0.001, n = 3). Atrogin mRNA was measured by real time PCR. Atrogin increased with wortmannin and 4-HT induced Foxo1/TSS nuclear translocation (*P < 0.001, n = 3) and decreased with IGF (*P < 0.05, n = 3). 4-HT had no effect on atrogin mRNA in vector control cells.