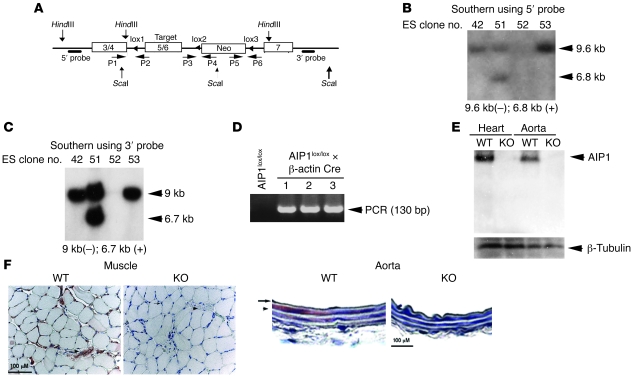
Figure 1. Generation of AIP1-flox and knockout mice.
(A) Schematic diagram for strategy to generate AIP1-flox mice. The targeting vector contains exons 3/4 at 5′ arm, exons 5/6 in the targeting region, and exon 7 at 3′ arm. PCR primers P1–P6 are shown. The 5′ probe with HindIII digest, and 3′ probe with ScaI digest are indicated. (B and C) Screening of ES clones. Genomic DNA from positive clones was extracted and used for Southern blot, using 5′ probe after HindIII digest (B) and 3′ probe after ScaI digest (C). Clone 51 was positive and used for blastocyst injection to generate chimera mice. (D) Generation of AIP1+/lox and AIP1+l– mice. The chimeras were mated with C57BL/6 for germline transmission to obtain AIP1+/lox. AIP1+/lox mice were further mated with β-actin Cre mice to delete both the targeting region (exons 5/6) and the Neo gene (AIP1+/– mice). KO mice were obtained by mating between the heterozygous (AIP1+/–) male and female. (E and F) AIP1 deletion in tissues. Muscle and aorta from WT and KO mice were homogenized and AIP1 expression was detected by Western blot with anti-AIP1 antibody (E). AIP1 expression in paraffin section of muscle and aorta was determined by immunohistochemistry with anti-AIP1 antibody (F). For muscle tissue, arrows indicate capillaries and the arrowhead indicates a large vessel. For aorta tissue, the arrow indicates endothelium and the arrowhead indicates smooth muscle layer.