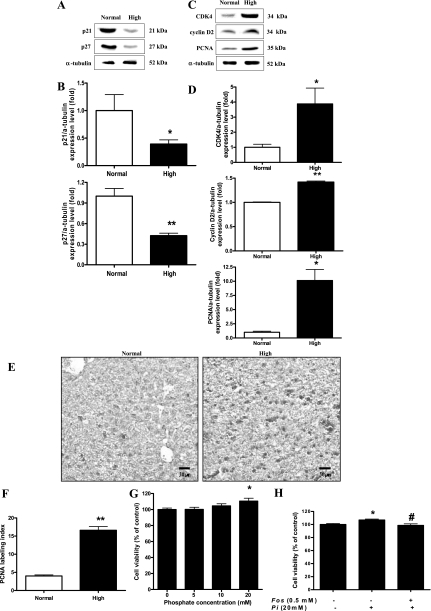
Fig. 6.
Effects of Pi on cell cycle progression in the liver. Two-week-old transgenic mice were fed a normal- or high-Pi diet for 4 wk. A: expression of p21 and p27 proteins in the liver. B: bands of interest were further analyzed by densitometry. C: expression of cyclin D2, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) proteins in the liver. D: bands of interest were further analyzed by densitometer. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with normal-diet group (means ± SE, n = 5). E: IHC of PCNA in the liver. Dark brown color represents PCNA protein in the liver. Original magnification was ×200. Scale bar = 50 μm. F: comparison of PCNA labeling index in the liver of young mice. PCNA-positive staining was determined by counting 3 randomly chosen fields per section, determining the percentage of DAB-positive cells per 100 cells at ×400 magnification. G: WB-F344 cells were incubated for 48 h with various concentration of Pi, and then, the cell viability was measured by MTT assay. H: WB-F344 cells were pretreated with 0.5 mM foscarnet (Fos) phosphate transport inhibitor for 30 min and then treated with 20 mM of Pi. After 48-h incubation with Pi, the cell viability was measured using MTT assay. Values represent the means ± SE of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with control, #P < 0.05 compared with Pi treatment.