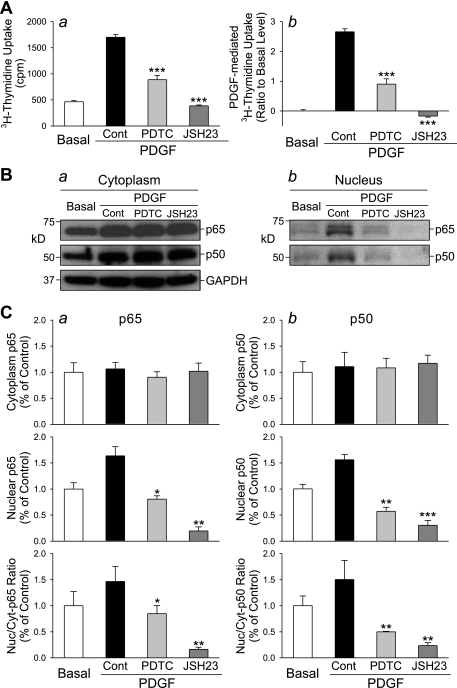
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation suppresses PDGF-induced PASMC proliferation. Growth-arrested PASMC were incubated in 0.1% FBS-DMEM, PDGF (10 ng/ml), PDGF+PDTC, and PDGF+JSH-23 for 24 h before [3H]thymidine uptake was measured. A: [3H]thymidine incorporation (a), measured as counts per minute (cpm), and PDGF-induced [3H]thymidine uptake (b, normalized to the basal level) in control cells (Basal, incubated in 0.1% FBS-DMEM) and cells treated with PDGF (10 ng/ml, PDGF-Cont), PDGF+PDTC (50 μM), and PDGF+JSH-23 (20 μM). ***P < 0.001 vs. PDGF-Cont. B: Western blot analysis shows the expression level of p65 and p50 in the cytoplasmic (a) and nuclear (b) fraction in PASMC before (Basal) and after incubation in the presence of PDGF (10 ng/ml, PDGF-Cont), PDGF+PDTC (50 μM), and PDGF+JSH-23 (20 μM). C: summarized data (means ± SE, n = 3 experiments) show the averaged protein levels of p65 (left) and p50 (right) in the cytoplasmic (Cyt-p65 and Cyt-p50, top) and nuclear (Nuc-p65 and Nuc-p50, middle) fraction and the ratio of cytoplasmic and nuclear p65 and p50 (bottom). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. PDGF-Cont.