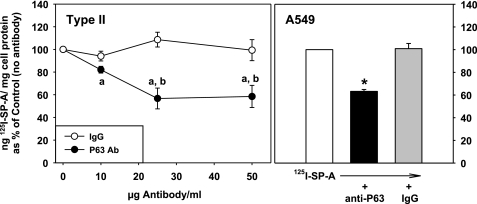
Fig. 7.
Ab to P63 inhibits the binding of SP-A to lung epithelial cells. Type II cells: cells were incubated without or with increasing concentrations of P63 Ab or nonimmune IgG for 15 min followed by the addition of 125I-SP-A (1 μg/ml) for 1 h at 4°C. The cells were harvested, and the binding of SP-A (ng 125I-SP-A/mg cell protein) was expressed as a percentage of the binding in the absence of Ab (171 ± 45 ng 125ISP-A/mg cell protein), which was set equal to 100%. Data are means ± SE, n = 3. “a,” Statistically significant difference from no Ab (100%); “b,” statistically significant difference from IgG. P < 0.05. A549 cells. Cells were incubated with no additions or with P63 Ab or IgG (25 μg protein/ml) for 15 min followed by the addition of 125I-SP-A (0.5 μg/ml) for 1 h at 4°C. The binding of SP-A (ng 125I-SP-A/mg cell protein) was expressed as a percentage of the binding in the absence of Ab (27.6 ± 2.3 ng 125I SP-A/mg cell protein), which was set equal to 100%. Data are means ± SE, n = 3. *Statistically significant difference from either no Ab or nonimmune IgG. P < 0.05.