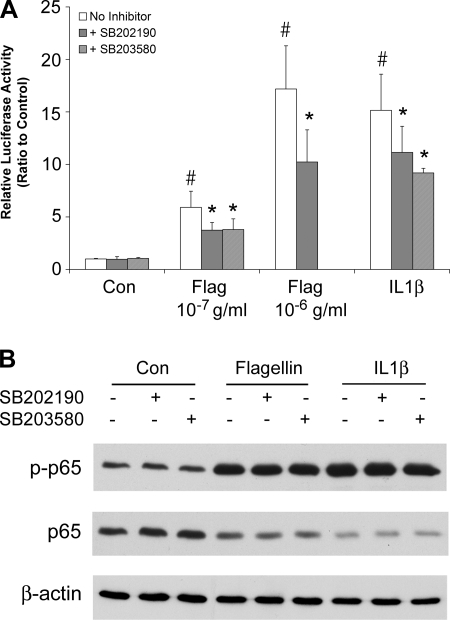
Fig. 9.
Effects of flagellin and IL-1β ± p38 blockers on NF-κB. A: luciferase. Confluent, NF-κB-luciferase-expressing Calu-3 cells were left untreated or exposed to S. typhimurium flagellin (10−7 g/ml or 10−6 g/ml) or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) alone or + p38 blockers (1 μM SB-202190, 5 μM SB-203580) for 4 h. NF-κB-activated luciferase activities were expressed relative to control, untreated cells. Each bar shows average ±SD of 3–8 different experiments for each of the treatments. #Significantly different from control, untreated cells for flagellin (P < 0.001) and IL-1β (P < 0.0001). *Inhibitor-treated significantly different from untreated for flagellin (P < 0.03 for SB-202190, P < 0.0001 for SB-203580) and IL-1β (P < 0.0007 for SB-202190, P < 0.05 for SB-203580). B: Western blots. Cells were treated with flagellin or IL-1β for 30 min ± SB-202190 or SB-203580, and Western blots of phosphorylated and total p65 were performed on cell extracts. Flagellin and IL-1β both stimulated phosphorylation of p65. There were no apparent effects of either blocker. Results are typical of 3 similar experiments.