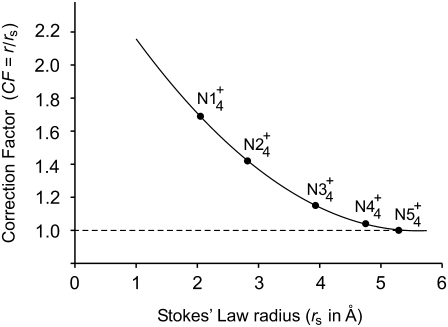
FIGURE 8.
Plot of the CF for small hydrated ions (≈≤5 Å), used for converting the Stokes' law hydrated radius, rs, to the effective hydrated radius, rH, for each ion. The Stokes' law radius was determined from measurements of limiting equivalent conductivity at 25°C using Eq. A7. This radius, rH, has been measured as the radius, r, of equivalent small tetra-alkyl ammonium ions of known molecular size, as indicated by the solid circles. The data values (r/rS) for these ions, where  to
to  represent
represent 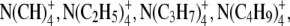 and
and 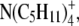 were taken from Table 4. The Stokes' law radius, rs, for these tetra-alkyl ammonium ions was recalculated using Eq. A7 from the limiting equivalent conductivity data at 25°C listed in Appendix 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22) (see text). The ionic radius, r, represents the actual radius of each ion estimated from molecular volumes or models and given in Table 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22). Note that above ∼5 Å, r ≅ rs. The value of r/rs can therefore be used as CF to determine the corrected equivalent Stokes' law radius for other ions, assumed to be the same as the ratio of the ionic radius determined from molecular models of the tetra-alkyl ammonium ions to their measured Stokes' law radius. The fitted curve was generated using SigmaPlot to enable the extrapolation of these values into the region required for ions of small hydrated size with an estimated Stokes law radius <2 Å. The graph therefore represents an extended and refitted version, with recalculated data (see text) of Fig. 6.1 of Robinson and Stokes (22).
were taken from Table 4. The Stokes' law radius, rs, for these tetra-alkyl ammonium ions was recalculated using Eq. A7 from the limiting equivalent conductivity data at 25°C listed in Appendix 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22) (see text). The ionic radius, r, represents the actual radius of each ion estimated from molecular volumes or models and given in Table 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22). Note that above ∼5 Å, r ≅ rs. The value of r/rs can therefore be used as CF to determine the corrected equivalent Stokes' law radius for other ions, assumed to be the same as the ratio of the ionic radius determined from molecular models of the tetra-alkyl ammonium ions to their measured Stokes' law radius. The fitted curve was generated using SigmaPlot to enable the extrapolation of these values into the region required for ions of small hydrated size with an estimated Stokes law radius <2 Å. The graph therefore represents an extended and refitted version, with recalculated data (see text) of Fig. 6.1 of Robinson and Stokes (22).