TABLE 5.
Parameters for determining the equivalent hydrated radius, rH, and equivalent hydrated diameter, dH, for the three alkali cations, nitrate, and chloride
| Ion | ri (Å) | di (Å) | λ0 | rs (Å) | CF | rH (Å) | dH (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | 0.60 | 1.2 | 38.6 | 2.39 | 1.57 | 3.74 | 7.5 |
| Na+ | 0.95 | 1.9 | 50.10 | 1.84 | 1.77 | 3.26 | 6.5 |
| Cs+ | 1.69 | 3.4 | 77.2 | 1.19 | 2.08 | 2.48 | 5.0 |
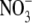 |
1.76 | 3.5 | 71.46 | 1.29 | 2.03 | 2.62 | 5.2 |
| Cl− | 1.81 | 3.6 | 76.35 | 1.21 | 2.07 | 2.50 | 5.0 |
Ionic radius, ri, and ionic diameter, di, data for the alkali cations and Cl− were from Pauling (43) (see also Table 3.1 in Robinson and Stokes (22)) and the 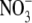 value was from Grunwald and Effio (44). λ0 values were from Appendix 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22). The Stokes' law radius, rs, calculated from limited equivalent conductivity using Eq. A7 in which rs = 92.1/λo assuming the viscosity of water, ηo = 0.008903 poise. The CF, determined from the fit of the tetra-alkyl ammonium ion data in Fig. 8, was calculated from rs using the fitted equation (A8) and the equivalent hydrated radius rH was determined by multiplying rs by CF (see text for details).
value was from Grunwald and Effio (44). λ0 values were from Appendix 6.2 of Robinson and Stokes (22). The Stokes' law radius, rs, calculated from limited equivalent conductivity using Eq. A7 in which rs = 92.1/λo assuming the viscosity of water, ηo = 0.008903 poise. The CF, determined from the fit of the tetra-alkyl ammonium ion data in Fig. 8, was calculated from rs using the fitted equation (A8) and the equivalent hydrated radius rH was determined by multiplying rs by CF (see text for details).
