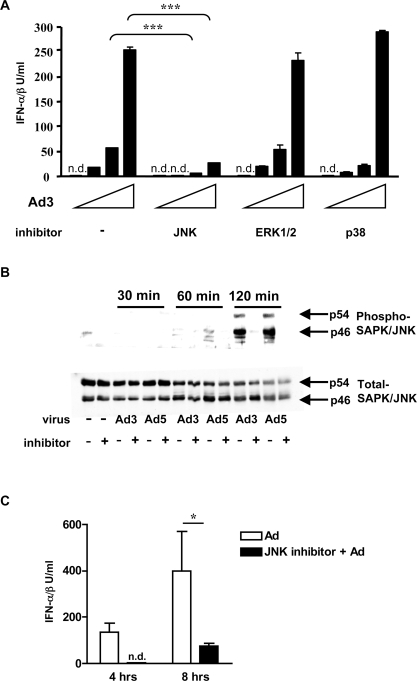
Figure 9. Adenovirus induction of IFN-αβ is dependent on SAPK/JNK signaling.
(A) Effect of MAPK inhibitors on the IFN-αβ response of BMDC to Ad. BMDC from mice were pretreated for 15 min with the inhibitor SP600125 (for SAPK//JNK), UO126 (for ERK1/2), SB 203580 (for p38) or with the diluent only as described in Materials and Methods, and then infected with 600, 1800 and 5400 Ad3 particles/cell or mock-infected. IFN-αβ was measured in cell-free supernatants 6 h after infection. n. d.: not detectable. (B) Inhibition of SAPK/JNK activation by SP600125 in Ad-infected BMDC. BMDCs were pretreated with SP600125) or with diluent for 15 min and then infected with 5400 Ad3 or Ad5 particles/cell, or were mock-infected. Total cell lysates obtained at the indicated times after Ad were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies to the total or phosphorylated p46 and p54 SAPK/JNK isoforms. (C) The effect of SP600125) treatment on the IFN-αβ production in Ad-infected mice. B6 Mice (4/group) were pretreated with the SP600125 inhibitor (20 mg/kg) i.p. or with diluent for 45 min and then infected with 3.6×1010 Ad5-GFP particles. Plasma IFN-αβ was measured 4 and 8 h after infection. One representative experiment of three is shown.